What parts does a car consist of? What does a car consist of? The principle of operation of the braking system.
The invention of the automobile radically changed human life, both in a positive and negative direction. Today, a car is not only a means of transportation, but also an indicator of status and position in society.
Almost every family has at least one car at its disposal, and there are also cities where there have long been more cars than people.
What does a car consist of?
Ask for a complete repair order describing the work performed. The order must include all repairs performed, parts installed by the shop, the cost of each part, labor costs, and the number of miles shown on the odometer when you delivered the vehicle to the shop and when Repair work completed Ask to be shown or given to you.
What are the consequences of deferring maintenance? There are several parts of your vehicle, which are interconnected. Failure to maintain can lead to problems: some specific parts may fail or the entire system may fail. Non-compliance simplest procedure maintenance, such as oil changes or coolant management, can result in poor fuel efficiency, poor drivability, or costly repair failures. This may void your warranty.
In order to understand how to drive a vehicle and how to operate it correctly, you need to know, at least, what it consists of and how it works. Every car owner has been interested in the design of his iron horse more than once. For some, basic knowledge is enough, while others prefer to study every detail of the car. Of course, in order to cover all the nuances of a car, you will need to at least write a book, but in order to understand the basics and know the basics, it is enough to read this article.
What guidelines should you follow to avoid costly repairs? Follow the manufacturer's suggested maintenance program according to your vehicle's use and as detailed in your vehicle's manual. Some repair shops have their own maintenance programs that require more service visits than those recommended by the manufacturers. Compare seminar service programs with your manual. Ask for explanations at the seminar - and be sure to understand them - to find out why they recommend doing more services than those recommended by the car manufacturer.
Perhaps for some, the design of a car is higher mathematics, but if you spend a little time and understand the essence, everything is quite simple. Now let's talk about everything in order.
1.Main components and systems
Despite the fact that today there is great amount different brands and car models, almost all of them are built on the same principle. We are talking about passenger vehicles. The car diagram is divided into several parts:
How to Protect Your Investment in Repairing Your Car
What are the warranties and service contracts that apply to auto repairs? There are no “standard warranties” for repairs. Make sure you understand what is covered by your warranty and ask to be put in writing. Please be aware that warranties may be subject to limitations, including factors such as time, mileage or mileage, deductibles, vendors authorized to perform work under the warranty, or special procedures required to collect claims.
To find out what your warranty rights are, read Warranties and Routine Automotive Service or contact your local consumer protection agency. Many car dealers and other dealers sell optional contracts - service contracts - operated by automakers or independent companies. Not all service contracts are created equal; prices vary and are usually negotiable. To decide whether to purchase a service contract, consider the following.
 Vehicle body or supporting structure. Today, the car body is its basis, to which almost all units and components are attached. The body, in turn, consists of a stamped bottom, front and rear side members, roof, engine compartment and other attachments. By attached components we mean doors, fenders, hood, trunk lid, etc. This division is quite arbitrary, since all the parts of the car are, one way or another, interconnected;
Vehicle body or supporting structure. Today, the car body is its basis, to which almost all units and components are attached. The body, in turn, consists of a stamped bottom, front and rear side members, roof, engine compartment and other attachments. By attached components we mean doors, fenders, hood, trunk lid, etc. This division is quite arbitrary, since all the parts of the car are, one way or another, interconnected;
If the contract's coverage overlaps with the coverage offered by another warranty. Procedures required to file a claim, such as prior approval for specific repairs or compliance with vehicle maintenance programs. If the company directly pays the repair costs to the workshop or if you must pay first and then process the refund. Reputation of the company offering the service contract. Check with the office about this. Attorney General State or local consumer protection agency.
- Its cost.
- Covered repairs.
- Where will the repairs be made?
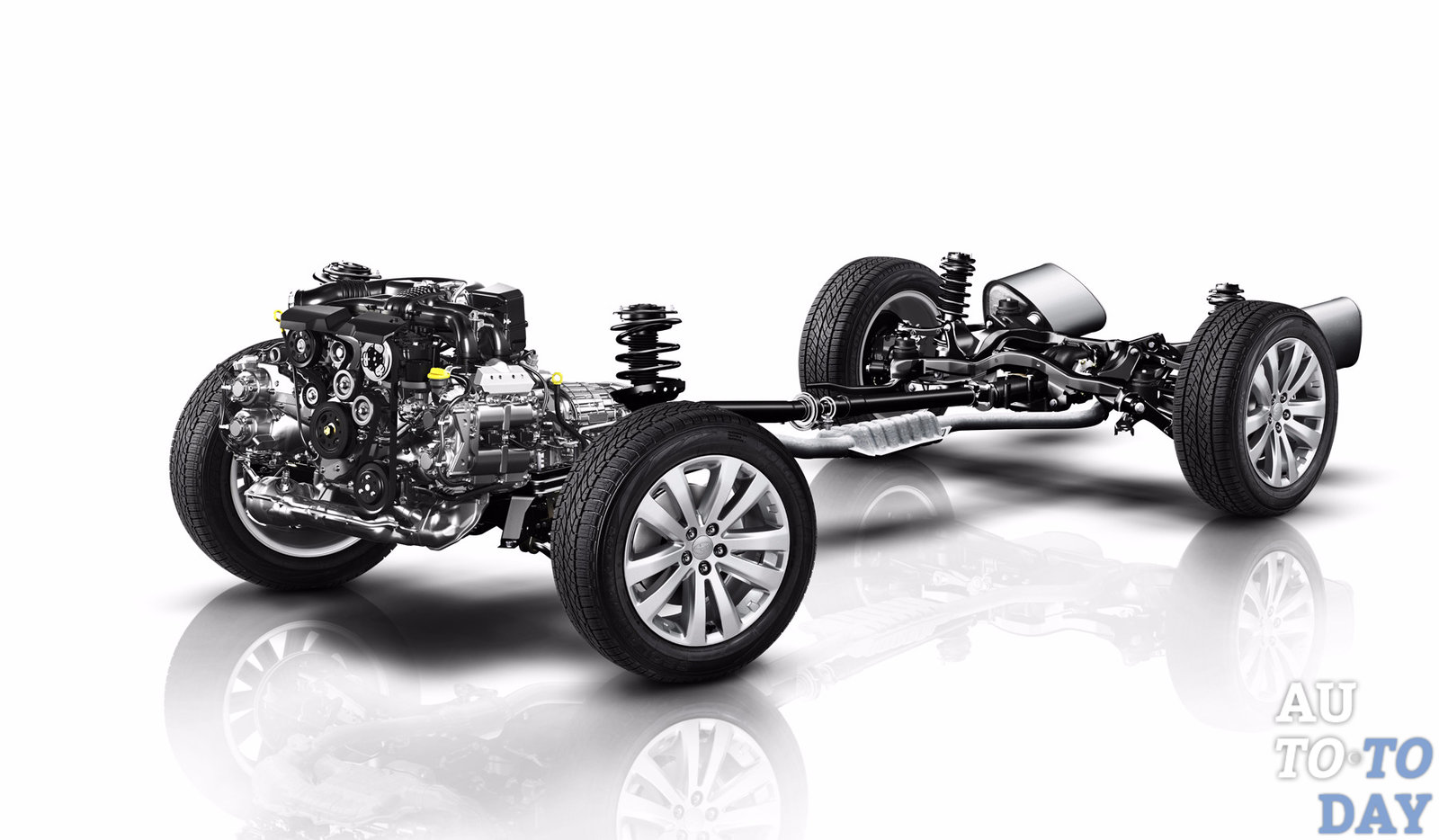 Chassis of the car. The name speaks for itself and suggests that the chassis consists of many components and assemblies with which the car is able to move. Its main components are considered to be front and rear suspensions, drive axles and wheels. The chassis of the car also includes the frame, to which most units are also attached. The frame is the predecessor of the body.
Chassis of the car. The name speaks for itself and suggests that the chassis consists of many components and assemblies with which the car is able to move. Its main components are considered to be front and rear suspensions, drive axles and wheels. The chassis of the car also includes the frame, to which most units are also attached. The frame is the predecessor of the body.
A car for dummies. Terminology
Document all transactions as well as your entire experience, taking into account dates, times, expenses, and names of people you dealt with. First, talk to your supervisor, administrator, or repair shop owner. If you cannot resolve your problem, contact your state attorney general's office or local consumer protection agency for assistance. These offices may have information about alternative dispute resolution programs available in your community. Another option is to file a claim in juvenile court.
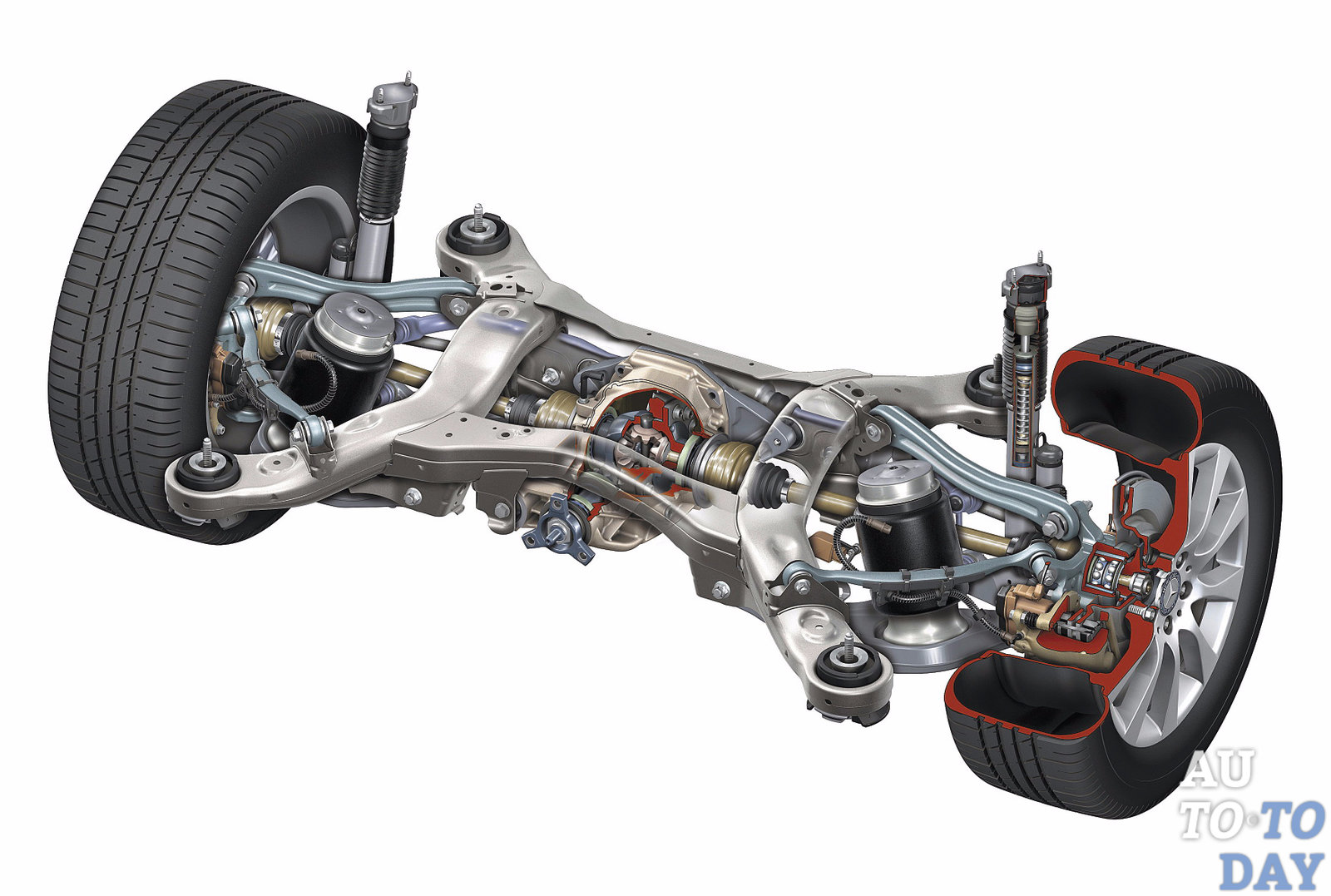 With the help of drive axles, the load is transferred from the frame or body to wheels and vice versa. As for the suspension, many cars have MacPherson strut suspension, which significantly improves vehicle handling. There are also independent (each wheel is individually attached to the body) and dependent (can be in the form of a beam or a drive axle, considered obsolete) suspensions;
With the help of drive axles, the load is transferred from the frame or body to wheels and vice versa. As for the suspension, many cars have MacPherson strut suspension, which significantly improves vehicle handling. There are also independent (each wheel is individually attached to the body) and dependent (can be in the form of a beam or a drive axle, considered obsolete) suspensions;
There is no need to hire an attorney for these types of lawsuits. The more you know about your car, the more likely you are to prevent repair problems. You can detect many of the most common problems by using your senses: observing the area around your car, listening to strange sounds, feeling some changes in the way you drive, or even noticing unusual smells.
Small stains or occasional fluids dripping under your car may not mean much. But stains of liquids or other liquids are worth considering; Control the composition of the drops immediately. You can identify liquids by their color and consistency.
Vehicle transmission. The transmission of a car is usually considered to be the power train. Its main task is to transmit torque from the crankshaft to the drive wheels. In turn, the transmission also consists of several parts, in particular the gearbox, clutch, driveline, differential, axle shafts and final drive. The latter are connected to the wheel hubs;
Yellowish-green, light blue, or phosphorescent orange spots indicate overheating or a coolant leak caused by a faulty hose, water pump, or radiator loss. A spot of dark brown or black oil fluid means the engine is losing oil. An oily red spot indicates a leak from the transmission fluid, power steering, or power steering. This may be due to normal condensation in your car's air conditioner.
- The loss may be due to gasket or sealant failure.
- Puddle clean water usually does not indicate any problem.
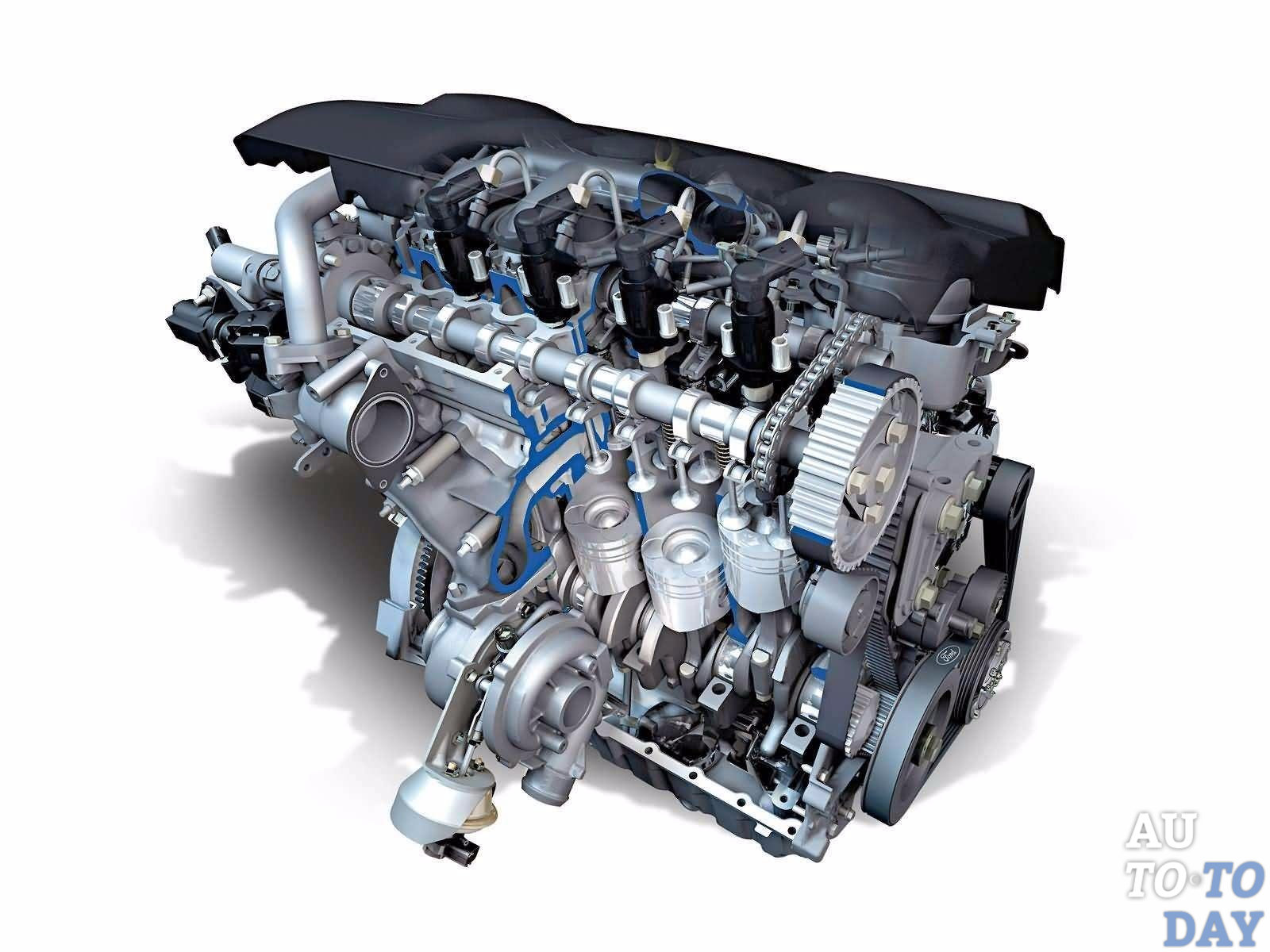 Car engine. The main task and purpose of the engine is to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. This energy is then transmitted through the transmission to the wheels of the car;
Car engine. The main task and purpose of the engine is to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. This energy is then transmitted through the transmission to the wheels of the car;
Control mechanism. Actually, the control mechanism itself consists of a brake system and a steering system;
Electrical equipment and control systems
The smell of burnt toast—a mild but pervasive odor—usually indicates an electrical short circuit and burnt insulation. To be on the safe side, try not to drive until you have been diagnosed with the problem. Rotten egg odor - a persistent odor of burning sulfur - usually indicates a problem in the catalytic converter or transformer or other emissions control devices. Look for signs of oil leaks. The smell of gasoline after an unsuccessful start may mean that the engine is “clogged” with fuel. Wait a minute before attempting to restart. If the smell persists, there may be a loss in the fuel system - a potentially dangerous problem that requires immediate attention. A burnt tar smell or an acidic chemical smell may indicate that the brake or clutch is overheating. Wait for the brakes to cool before repeating hard braking on mountain roads. If a little smoke comes out of the wheels, it means the brake is stuck. In this case, you will need to have the vehicle towed to recover it. A sweet smell indicates loss of coolant. If the temperature marker or warning light does not indicate overheating, carefully take it to the nearest service station while checking your temperature marks. If this smell is combined with another metallic smell and there is smoke or steam under the hood, the engine will overheat. Continued driving under these conditions could cause serious engine damage. You have to pull the car out to restore it.
- Do not delay diagnosis and repair.
- A thick, acidic smell usually means burnt oil.
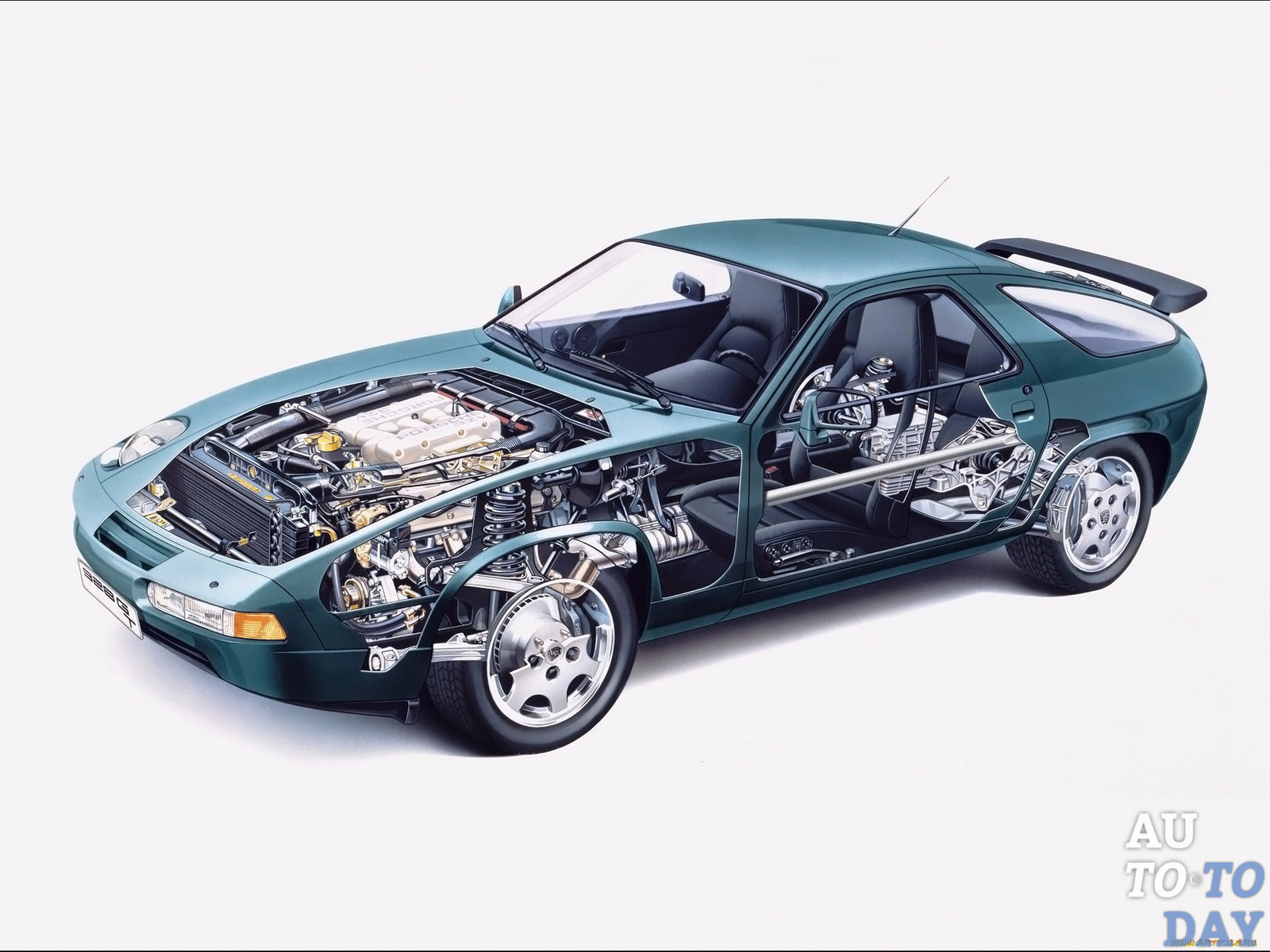 Electrical equipment of the car. No modern car can do without electrics, the main parts of which are the battery, electrical wiring, alternator and engine management system. These are only the main parts of the car, each of which provides a system within a system and sometimes more than one. Some parts are worth going into more detail.
Electrical equipment of the car. No modern car can do without electrics, the main parts of which are the battery, electrical wiring, alternator and engine management system. These are only the main parts of the car, each of which provides a system within a system and sometimes more than one. Some parts are worth going into more detail.
These are the most common noises and their meanings. The directional, ventilation or climate tape is loose or worn. . Press - A small sharp noise related to the engine or vehicle speed may indicate. This can be caused by brake wear indicators that alert you that it's time for maintenance. Install the joint or other transmission line or steering component.
- Loose cap or ring.
- The fan blade is weakened or bent inward.
- The shut-off valve is blocked or low level engine oils.
- Faulty exhaust pipe, transformer or damper.
2. Brief overview of types of motors
First of all, it is worth noting that the engine and motor are one and the same. Motors are often called internal combustion or electric engines. It is no secret that the engine serves as a source of energy to move the vehicle. Most cars have internal combustion engines, which can be roughly divided into:
- This is usually caused by using gasoline with a lower gasoline content.
- Check the correct octane position.
- If the problem persists, the engine may fail to ignite.
- Worn crankshaft or misaligned connecting rod or connecting rod.
- The transmission torque is loose or disconnected.
- Free shock or other suspension component.
- Muffler or exhaust pipe.
Piston engines, in which expanding gases during fuel combustion force the piston to move, which in turn drives the crankshaft of the car;
In rotary engines, the same gases drive a rotating part, the rotor itself.
If you go deeper, there is a large number of types and subtypes of engines. Based on the type of fuel, engines can be divided into diesel, gasoline, gas and gas generators.
Worn shock absorbers or other suspension components - or improperly inflated tires or tires - can lead to poor turning ability. While there is no set formula for replacing shock absorbers, try this: bounce the car up and down each wheel, then bounce it alone. If the shock absorbers are worn, the car will only bounce once or twice. Generally, a vehicle's rubbers or springs do not wear out and there is no need to replace them unless one of the vehicle's corners is lower than the others. Overloading your vehicle can damage your suspension. Balance your tires or tires correctly. An improperly balanced or unbalanced tire causes vehicle vibration and can prematurely wear steering and suspension components. Check how many times the car bounces. . Brake problems have several symptoms.
There are also gas turbine internal combustion engines, electric, orbital, rotary, rotary-vane, etc. Today, the most common is the piston internal combustion engine.
3. Brief overview of types of checkpoints
A gearbox or gearbox is one of the main parts of a car's transmission.. Basically, checkpoints are usually divided into three types, namely:
Schedule diagnostics and repairs if. The brake pedal remains locked to the floor when she maintains pressure on the pedal.
- When applying the brakes, the vehicle veers to the side.
- You hear or feel a rubbing or grinding noise when braking.
- The brake indicator lights up on the dashboard.
Excessive oil consumption. The engine continues to run after the ignition key is removed.
- Trouble starting or running the engine.
- The check engine light on the dashboard comes on.
- If it gets stuck suddenly or goes out.
- Poor or insufficient acceleration.
- Low fuel efficiency.
Manual Transmission. The principle of its operation is that the driver uses a lever to change gears, while constantly monitoring the engine load and vehicle speed;
An automatic transmission eliminates the need to constantly monitor speed and load, and there is no need to constantly use the lever;
A robotic gearbox is a semi-automatic type of gearbox that combines the properties of a manual and automatic gearbox.
In fact, there are many more types and subtypes of checkpoints. So, they distinguish Tiptronic(basis - automatic transmission with manual gear selector), DSG(equipped with 2 clutches, has an automatic shift drive and is a 6-speed gearbox) and variable speed drive(continuously variable transmission).
4. Brake system
As the name suggests, the braking system is designed to reduce the speed of the car or stop it completely. The brake system consists of brake pads, discs, drums and cylinders. Conventionally, the braking system can be divided into two types - working (designed to completely stop or reduce speed) and parking (designed to hold the car on uneven or difficult road surfaces).
Modern cars require the installation of braking systems, which consist of brake mechanisms and hydraulic drive. When you press the brake pedal, excess pressure arises in the hydraulic drive, which occurs due to the brake fluid. This, in turn, triggers other braking mechanisms.
5. Clutch
If we talk in simple words, the clutch is designed to a short time disconnect the engine from the transmission, and then reconnect them. The clutch consists of a clutch mechanism and a drive mechanism. The drive is designed to transmit forces from the driver to a specific mechanism. In a car, each mechanism has its own drive, thanks to which it comes into action.
The clutch mechanism is a device in which the process of transmitting torque through friction occurs. The components of the clutch mechanism are the crankcase, casing, drive, driven and pressure plates.
 All of the above is just the tip of the iceberg, since each of the points contains dozens more sub-points. For a general understanding of the structure of a car, it is enough to know its main components and assemblies. Now you know exactly how and why your car moves, brakes and consumes gas.
All of the above is just the tip of the iceberg, since each of the points contains dozens more sub-points. For a general understanding of the structure of a car, it is enough to know its main components and assemblies. Now you know exactly how and why your car moves, brakes and consumes gas.
Subscribe to our feeds at
Car design for beginners
Automobile, in fact, consists of of three parts: engine, chassis And body.
One of the most important details is engine– this is the heart of the car. An internal combustion engine drives a car by converting the energy of fuel combustion into mechanical work.
Chassis– the basis of the car consists of several parts:
- transmission
- chassis
- governance mechanisms.
What is a transmission?
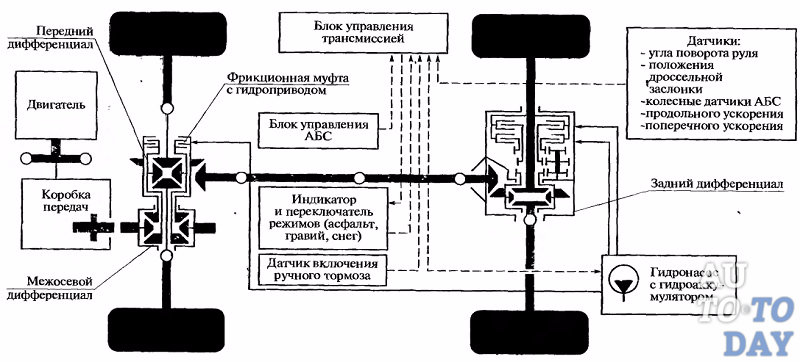
Transmission This is a whole system of mechanisms that transmits driving force from the car engine to its wheels. TO transmissions The following mechanisms include:
1. Transmission– allows the car to move backwards ( reverse), disconnects the drive wheels and the motor, and also, if necessary, changes the torque.
2. Clutch– located between the engine and gearbox. Responsible for connecting and timely disconnecting the engine from other devices and transmission elements.
3. Transmission allows you to change the torque if necessary, disconnects the engine and the drive wheels, and is also responsible for the “reverse gear” of the car.
4. main gear transmits torque to the drive shafts and increases it.
5. Cardan transmission is responsible for transmitting torque from gearboxes directly to final drive.
6. Differential. Thanks to it, the driving wheels of the car do not move equally, which is necessary when the car is moving on uneven surfaces, bumps, and turns.
7. Half shafts or drive shafts wheels provide torque transmission from differential to the driving wheels of the car.
Chassis.
Chassis- the basis of the car, all the mechanisms of the main systems are attached to it, as well as chassis determines the functional affiliation of the car and its appearance. The running gear may include suspension, wheels, car body.
Body.
The body serves to accommodate passengers. Basic body types passenger car: sedan, hatchback, railway carriage, cabriolet, limousine etc. Depending on the structure of the machine inside car body you can find a wide variety of equipment and devices that significantly increase the level of safety and comfort of passengers.
Starting device for auto
Starter is a powerful DC electric motor, it is this that starts ICE. When the ignition key is turned from the “start” position, current through the relay from the battery is supplied to the starter windings and starts the engine.
Starter operating stages:
Using the starter drive mechanism, the gear on the armature shaft meshes with the flywheel ring gear
The gear rotates together with the starter armature shaft and thereby turns through the flywheel crankshaft engine, the engine starts.
After starting work ICE the drive device removes the gear starter out of engagement with flywheel ring gear.
Considering the general structure of the car, it is impossible not to touch upon engine operating principle.
The basis of any work internal combustion engine is the ignition of a certain amount of high-energy fuel in a confined space.  During the combustion of fuel, a large amount of energy is released, which heats the gas inside the cylinders, accordingly increases the pressure, and due to the pressure difference (under the piston it is normal, but the compression in the cylinder due to fuel combustion is several times higher) the engine piston begins to move.
During the combustion of fuel, a large amount of energy is released, which heats the gas inside the cylinders, accordingly increases the pressure, and due to the pressure difference (under the piston it is normal, but the compression in the cylinder due to fuel combustion is several times higher) the engine piston begins to move.
In order for the engine to continuously produce mechanical energy, the combustion chamber must be cyclically filled with a fuel-air mixture. As a result of this, the piston causes the crankshaft to move, which is responsible for the movement of the car's wheels. Most modern engines are four-stroke in their cycle. The energy obtained from burning gasoline is almost completely converted into useful energy. Four-stroke engines are called because the full cycle takes place in four parts of equal time, after which everything is repeated.
How the engine works.
Release stroke
The piston is directed to the highest point and at this time the exhaust valve opens and the piston pushes the exhaust gas into the exhaust pipe, while the end continues to rotate by inertia. As soon as the piston reaches the top point, the exhaust valve closes.



















