Why do gums fester and how is this disease treated? How is periodontitis treated in dentistry? Why granuloma cannot be ignored
In the initial stage of purulent inflammation of the gums, symptoms do not appear, which often does not allow diagnosing the problem in time.
Pus in the gums may indicate pain during chewing and bleeding during hygiene procedures.
It is possible that pus will be released from under the gums when you press on the problem area.
The main reason that pus comes from the gums is infection. It gets there in various ways; the periodontal canal is an area that is quite difficult to care for.

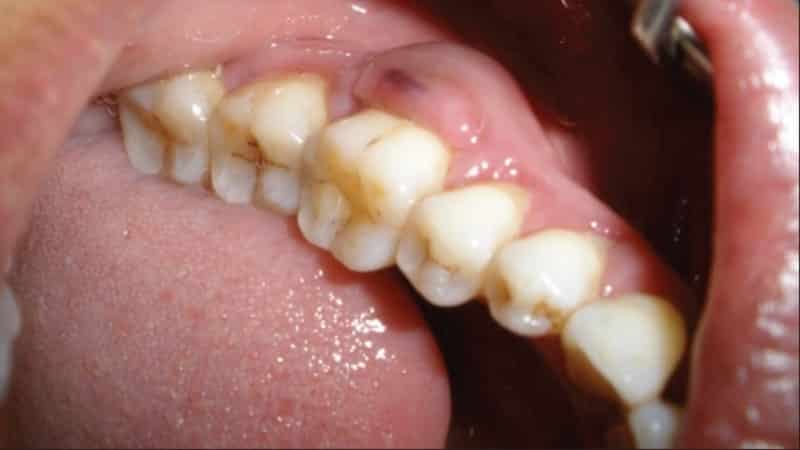
Pus in the gum
Especially if the teeth are located at some distance from each other, there are frequent inflammations of the oral cavity.
There is a space between the elements of the dentition and the gum; it is filled with food debris, which over time begins to rot.
Frequent reasons for the gums near the tooth to fester are:
- periodontal inflammation – it is formed due to the exposure of the neck of the tooth as a result of detachment of the gum tissue;
- periodontitis is an inflammation of the area at the apex of the tooth root, formed as a result of a poorly placed filling, advanced caries, and;
- – trophic damage to the gums, which leads to tooth loss. It develops due to improper oral hygiene. Its development is facilitated by decreased immunity, hereditary factors are possible;
- – develops due to improper oral hygiene, accompanied by poor-quality orthodontic treatment.
This leads to the problem of injury, which is caused by tissue damage from a tooth fragment or an inconveniently installed crown. You can damage your gums with a toothpick if you use it carelessly, or with a toothbrush that is too hard.
Pus on a child’s gums can form due to injury or damage to soft tissues with sharp objects.
If you have problems with your gums, you should immediately visit your dentist. Neglected trauma to the gum canal and the accumulation of pus in it can lead to the spread of infection through the blood and lymph throughout the body.
Pus in the gums: treatment
Suppuration in the gums is a process that can lead to blood poisoning and even cause death.
When pus has formed in the gum, what should a specialist tell you to do, having studied the problem and drawn up a competent treatment plan. Initially, he will conduct an examination and prescribe medications that will stop the disease.
An abscess on the gum is usually removed surgically
At the first appointment, the doctor removes the enamel from the surface. If there is an abscess, manipulations must be carried out to remove it surgically, then antibiotics can be used to stop the inflammatory process and folk remedies for local use (lotions, compresses).
If pus comes out of the gums on its own, you shouldn’t worry about it. This does not mean that the problem is solved; the inflammation will continue if drug treatment is not carried out.
You cannot prescribe medications on your own, especially antibiotics. Uncontrolled use of medications will lead to new health problems.
 When pus comes from the gums - what to do when you can’t get to the dentist?
When pus comes from the gums - what to do when you can’t get to the dentist?
Local anesthetics and disinfectants can be used.
A decoction of chamomile, yarrow, and calendula has antiseptic properties. Chlorhexidine helps a lot.
If pus comes from the gums near the tooth, treatment requires the use of cold, it reduces the rate of inflammation and relieves pain. If the pain is severe, you can take medicine.
It is worth remembering that applying cold to a sore spot is a contraindicated technique in the question of how to draw out pus from the gums. You should not get carried away with self-medication, this can lead to the exacerbation being asymptomatic, and blood poisoning will begin.
When treating a purulent process in the gums, it is necessary to constantly keep the oral cavity clean. Rinse and brush your teeth after every meal, otherwise food residues will further provoke the rotting process.
How to remove pus from the gums at the root of the tooth?
When treating an abscess located at the root of the teeth, two treatment options are used: conservative and surgical.
The surgical method is simpler and faster. In some cases, the tooth may not even be touched; the root canals are cleaned and treated using an apex resection procedure.
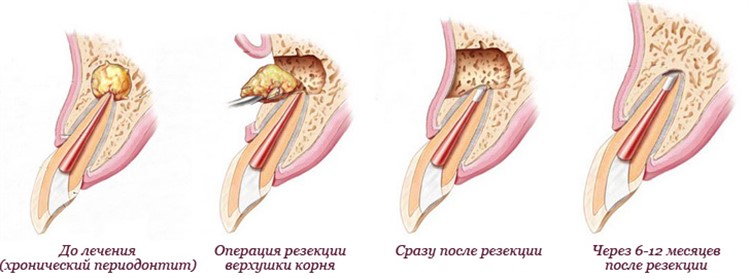
Root apex resection
This method is suitable in cases where only the root canals at the apex of the root are poorly sealed, and there are no problems in other places.
The essence of the procedure is to cut off the apex of the root in a part of the unsealed canal using a drill, clean out the granuloma, pump out the pus, and remove the cyst on the gum. There is no need to open the tooth.
 The surgical method has its advantages, these include:
The surgical method has its advantages, these include:
- A small number of visits to the dentist. At the first appointment, the abscess on the gum is opened, then medication is prescribed home treatment. After eliminating the inflammation, an operation is performed, which takes no more than 50-60 minutes;
- There is no need to remove the old filling or crown, which reduces the cost of treatment and prevents repeated prosthetics and fillings.
Conservative treatment begins with a visit to the X-ray room, where an image of the problem part of the jaw is taken. If a problem is detected, conservative treatment is prescribed.
 If there is a filling on the tooth, it is removed, the root canals are expanded, the affected areas are cleaned, and nerves are removed if necessary.
If there is a filling on the tooth, it is removed, the root canals are expanded, the affected areas are cleaned, and nerves are removed if necessary.
When the pus on the gum above the tooth is removed, antibiotic treatment is prescribed.
If there is swelling, the person is sent to a surgeon, who makes an incision and opens the abscess. After treatment, the canals can be filled.
Before this, an x-ray is taken again to make sure that the problem has been solved and the pus from the gums near the tooth has been removed.
In difficult cases, when a cyst has formed on the upper part of the root, after treatment a temporary filling made of medicinal material is placed. After three months, a control photograph is taken, the temporary material is removed, and the tooth is permanently filled.
Treatment tactics for periodontitis
 For periodontitis, the treatment tactics are similar to the treatment of purulent inflammation at the roots of the teeth, but there are some differences.
For periodontitis, the treatment tactics are similar to the treatment of purulent inflammation at the roots of the teeth, but there are some differences.
It begins with a visit to the periodontist. The doctor sends the patient for an x-ray, where a panoramic image of the area of inflammation is taken.
It shows the volume of the lesion, the depth of the gum pockets. Based on the results of the image, a treatment plan is drawn up, which may include depulpation of one or more elements of the dentition.
There are chronic and localized periodontitis. If the inflammatory process covers the area of one or two teeth, the disease is considered localized.
If several teeth are affected, the disease is called generalized periodontitis. In this case, the gums and periodontal pockets rot.
Treatment of chronic and localized periodontitis is almost identical.
It is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes in the area where gum pockets are located, the only difference is how many teeth are affected and require the attention of a specialist.
Treatment begins with cleaning the teeth and gums from plaque, treating the periodontal canals with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medications.
Antibiotics may be prescribed. The initial task is to eliminate inflammation and pus formation, after which the doctor can begin the actual treatment.
It consists of surgical curettage of periodontal pockets. This procedure allows you to remove inflammatory granulations that contribute to the production of pus.
In some cases, bone grafting is performed to reduce the depth of the gum pockets.
Video on the topic
Operation to remove pus from the gums:
Many people often ignore pus in the gums, believing that everything will go away on its own. This is the wrong approach; the presence of an abscess indicates the presence of an oral cavity problem. If treatment is not started in time, the problem will lead to dangerous complications. Timely treatment will preserve the health of your teeth and gums.
Tooth root granuloma is a dangerous, complex and quite serious disease. Most often it occurs as a result of complications. Granuloma has its own peculiarity. First, the inflammatory process begins, which does not cause unpleasant symptoms. Then the disease makes itself felt with sharp pain. What kind of sudden illness this is, we’ll figure it out below.
From a physical point of view, a granuloma is a small dense nodule located at the very base of the tooth, in the periodontium. It can have dimensions from 5 to 8 mm. Sometimes a granuloma is compared to a cyst, inside of which there are dead bacteria.
The formed granuloma is the epicenter of the disease. From there, the inflammatory process goes further and destroys healthy tooth tissue. Such a focus of infection cannot be left without treatment. In the process of its further development, it will certainly lead to disruption of the functioning of the body’s organs. In most cases, inflammation spreads to the facial and neck muscles, as well as to the heart area.
How does a tooth root granuloma form?
Granuloma has the following development mechanism:
- The first stage: the appearance of a dental disease and bringing it to an advanced state. The presence of a long inflammatory process leads to the formation of pulp large quantity microorganisms. The inflammatory process occurring in the pulp gradually leads to its death.
- Second stage: microbes go into further action. Gradually, the infection enters the bone tissue area. As a result, a new formation appears, which gradually turns into the granuloma in question.
- The third stage: the bone begins to retreat from the source of infection, a capsule of connective tissue is formed at this site, quite dense in structure. A serious inflammatory process continues inside the capsule, as a result of which bacteria rapidly multiply. The stage is characterized by rapid tissue growth. Over time, the bacteria turns into pus. If you consult a doctor for last stage, he will diagnose “acute granuloma”.
The disease greatly aggravates weakened immunity. Against this background, the tooth becomes abnormally mobile. Eventually its roots will be exposed.
Infections reach the tooth root in another way: through periodontal pockets. These pockets appear when hard tartar forms. The stone contains a huge variety of bacteria. They provoke the appearance of a gap between the socket and the gum. It is through this that the infection goes to the root. At the very base of the root, tissue grows that is completely filled with pus. This granuloma.
Causes of granuloma
Granuloma occurs after the following factors:
- Untreated caries.
- Untreated, which appeared against the background of an inflamed pulp.
- Inflammatory process in the periodontium (the tissue that surrounds the tooth).
- A tooth fracture that results in infection in the internal area.
- Poor tooth antiseptics, which over time led to infection.
- Poor quality antiseptic treatment after pulp removal.
- Poor quality antiseptic treatment after root canal treatment.
Secondary causes of granuloma:
- Stress.
- Severe physical stress.
- Sudden climate change.
- Severe hypothermia.
- Serious cold infection.
The inflammatory process of periodontium can begin as a result of improper treatment. For example, even due to unprofessional dental filling.
Often the disease occurs after tooth extraction. Why? The disease appears against the background of inflammatory processes and a complete lack of necessary preventive measures. Over time, the site of the extracted tooth begins to be covered with tissue. Microbes quickly get inside it, which leads to further periodontal inflammation. If prevention is not done, the granuloma will quickly grow and fill with pus. If treatment is neglected, the granuloma will begin to move along the entire length of the gum. This course of the disease leads to infective endocarditis, a rather dangerous disease that often ends in death.
Granuloma often occurs after the removal of children's baby teeth. Childhood does not mean that the patient cannot have granuloma.
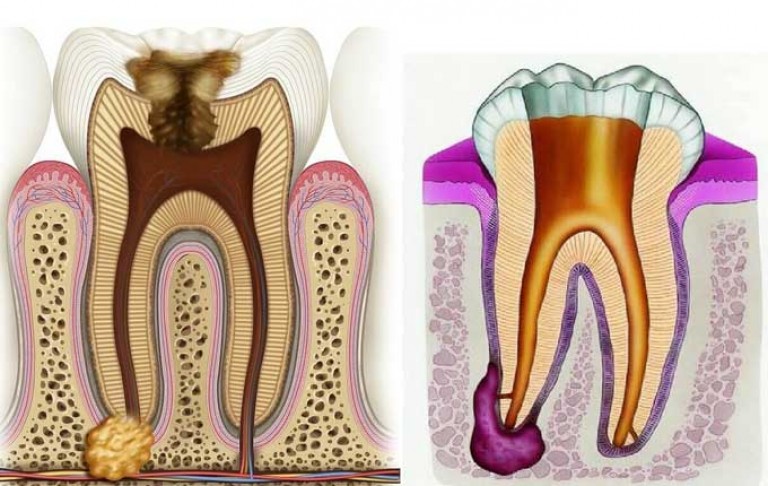
Symptoms of granuloma
The granuloma begins to be asymptomatic. Then comes a certain stage at which the body signals the disease with sharp pain (the first symptom).
Another symptom of the disease is the presence of a foreign body in the oral cavity. This is tissue that has grown greatly as a result of inflammation. It can be easily felt with the tongue.
When the granuloma becomes visible visually, the disease begins to be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Redness of the gums.
- Swelling of the gums.
- Inflammation of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature.
- Darkening of the enamel.
- The appearance of pus between the tooth and gum.
- Headache with severe malaise.
- Flux.
Swelling and redness can be on different sides of the tooth. For example, from the inner surface of the gum, from the palate or behind the lips.
When pressing on the inflamed area, the pain intensifies greatly. It has a bursting character and only grows over time.
Let's summarize. The first symptom of granuloma is acute pain. It is accompanied by slight swelling. The next stage is accompanied by sudden changes in body temperature.
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can make a correct diagnosis based on an x-ray. In the picture you can see a small darkened area near the root of the tooth.
Radiovisiography can also be done in the hospital. This is a type of x-ray with less radiation. The results are assessed not in the picture, but on the monitor screen. For this reason, such a survey is often called digital.
Granuloma is best recognized at the first stage. It is often detected during the treatment of other dental diseases. In addition, doctors pay attention to abnormal swelling of the gums, which is very painful. Also, the protrusion of bone near the apex of the tooth comes to the attention of doctors.
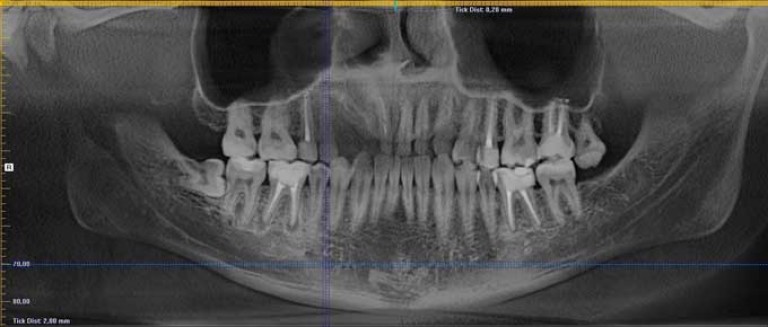
Treatment of granuloma
From the above it is clear that treatment should begin at the first stage. The patient’s first action is to come to the clinic. The second is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and undergo an x-ray examination. Third, remaining calm during treatment.
Treatment can be of three types:
- Conservative or therapeutic.
- Surgical.
- Folk.
The most effective are the first two types. They are performed in a hospital setting. Traditional treatment is more supportive in nature.
Conservative treatment
Such therapy includes taking antibacterial, sulfonamide drugs and tooth filling. Such treatment stops the progression of granuloma and saves teeth from the process of destruction.
Antibiotics help to immediately stop the disease, remove painful microflora and rid the tooth of infection. While taking medications, the doctor also prescribes additional rinses for mouth antiseptics. Anesthetic medications help relieve pain.
In case of deep caries, the pulp is inflamed, the dentist cleans the canals and removes the source of infection. Next, the doctor applies medicine deep into the tooth and installs a temporary filling. After some time, a permanent filling is placed in this place.
In severe cases, therapeutic treatment is pointless. Then the tooth affected by granuloma is treated surgically.
Surgery
The essence of this intervention is to open the gums, from which pus is subsequently removed using drainage. As a result, the tissue becomes non-inflamed. In parallel with surgery, antibacterial drugs, painkillers and antiseptics are prescribed.
The prognosis after surgical treatment is always favorable.
Surgical treatment consists of one of the following procedures:
- Opening followed by drainage.
- Resection of the apex of the tooth root.
- Removal of a tooth.
If there is a pocket on the gum or a gap on the tooth, then the cyst is dissected, from which the substance located there is removed.

Root resection
Root resection consists of the following steps:
- Opening the shell.
- Channel cleaning.
- Filling with medicinal solution.
- Removal of the granuloma itself and the affected apex of the tooth.
- Replacing the inflamed tissue that has been cleaned out with new artificial tissue.
- Filling a tooth.
Hemisection of tooth
The operation is performed if the tooth has many roots and the disease has reached such a stage that it is impossible to save the root. Hemisection of a tooth consists of the following stages:
- Complete removal of the root and the coronal part that is adjacent to it.
- Filling an empty cavity with a special dental material.
- Installation of a crown.
- Control of the tooth after surgery using x-rays.
Removal of a tooth
When a tooth cannot be cured, it is removed. Removal is carried out in the following cases:
- If the patient has prolonged illness.
- If a gum pocket begins to form.
- If there is a vertical crack on the tooth.
- If the tooth is completely destroyed or the crown is destroyed.
- Perforation of the root is visible.
- The root canals are impassable.
Traditional treatment
People use several recipes to alleviate the condition of granuloma:
- Preparation of tinctures with propolis and calamus. You will need 30 g. dry propolis and 30 gr. calamus roots. The ingredients are poured with vodka and infused for 2 weeks. Used for rinsing.
- Herbal decoctions: eucalyptus, chamomile, sage. Used for rinsing.

Complications
Untreated granuloma leads to:
- To complete loss of a tooth. This happens due to complete destruction of the root. As a result, soft tissues are drawn into the inflammation process, in which pus accumulates.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- Formation of a dental cyst.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Infection of other organs and the development of sinusitis, pyelonephritis and infectious myocarditis.
- If pus gets into the skull, meningitis, encephalitis and inflammation of the peripheral nerves may begin.
- The appearance of migratory granuloma. Manifests itself in the form of protrusion of the facial skin. The disease also appears in the form of abscesses in different places.
Prevention
Preventive measures must be carried out in a complex manner. They should be aimed at preventing the occurrence of the disease. Preventive actions include the following:
- Constantly maintaining cleanliness of the oral cavity. That is, this is daily, high-quality cleaning and rinsing.
- Treat bleeding gums.
- Scheduled visit (2 times a year) to the dentist.
- Change your toothbrushes regularly to avoid spreading infections in your mouth.
- The slightest pain in a tooth should prompt the patient to immediately go to the hospital. The process cannot be delayed.
- convert Special attention for diseases such as caries, pulpitis and periodontitis, which are common causes of granuloma.
- Use only medicated toothpastes as a preventive measure.
- Regularly rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions.
- Eat food with the maximum content of calcium, trace elements and vitamins.
What is the forecast
The prognosis of treatment always depends on the severity of the disease. Everything influences: the stage of development, complexity and methods used in treatment. Treatment in the first stages of the disease always gives only a positive prognosis. Antibiotics and therapy always help. Granuloma in childhood also responds well to treatment.
If the granuloma is at the stage of pus appearing, success depends on where the source of inflammation appears. If it is the root of a tooth, then most likely the prognosis will be unfavorable and the tooth will have to be pulled out. If, then the contents are cleaned using drainage. The patient is also prescribed a course of antibiotics.
Failure to treat granuloma may well lead to death. Like this? The resulting pus penetrates the muscles and enters the heart area. The result is sepsis, which leads to death.
Yes, granuloma is a completely unpleasant and dangerous disease. If this is the initial stage, then there is no need to worry. You should go to the hospital without hesitating for a minute. The patient must try to avoid extreme stages.
An abscess is a common oral disease. A capsule with pathological fluid forms on soft tissues, often in the area of the tooth root. What follows is an acute infection of the area and the body, which is manifested by multiple symptoms. In the article we will look at what a tooth abscess is (photo below), why it occurs, what symptoms it is accompanied by and what treatment it requires in classical medicine or at home using folk recipes.
Causes of the disease
Tooth abscess
The reasons for the accumulation of pathological microflora in enamel cracks or gum pockets are as follows:
- an old toothbrush that is unusable;
- poor quality toothpaste, which does not fulfill its assigned functions of cleansing teeth and gums from carious manifestations and microbial plaque;
- accumulation of food in the interdental space and at the base of the tooth, which leads to the process of decay and the formation of a large number of bacteria on the surface of the teeth.
Eating too hot or cold food, spicy, sour and sweet dishes can lead to the appearance of microcracks in the enamel, which is accompanied by increased sensitivity and the development of pathological processes.
First of all, purulent and other infections occur in the oral cavity in the absence of regular and high-quality hygiene.
The more pathogens that accumulate in the mouth, the higher the chance of an abscess.
Another reason for this pathology– dental diseases in a recurrent form, as well as poorly treated. If you have pulpitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease, gingivitis, deep caries, granulomas or cysts, then the risk of developing an abscess increases significantly.
Also, any mechanical injuries in the area of soft tissues or teeth (jaw fracture, bruise, blow, chipped and tooth decay) can cause suppuration of the area.
Interestingly, even systemic diseases that are not related to the dentition can cause an abscess. Firstly, during the disease the immune system is significantly weakened and cannot fight the infection. Secondly, viruses and microbes that cause a systemic disease (for example, influenza, ARVI, sore throat, bronchitis, etc.) spread through the circulatory system throughout the body.

Abscess after tooth extraction
The warning signs of an abscess are cysts, boils, granulomas and other formations on the mucous membrane. Ordinary stomatitis or herpes can also be complicated by the appearance of a capsule with pus.
In rare cases, an infection enters the body due to the negligence of a dentist, for example, after an illiterate injection of an anesthetic into soft tissues.
These reasons lead to a violation of the integrity of the mucous surface and enamel, which means that pathological microflora has free access to the pulp and gingival pockets. If the disease is not cured in time, the inflammatory process spreads to neighboring tissues and even bone.
Symptoms of the disease and types of abscess
The abscess itself is an infectious formation on the mucous surface, inside which pathological fluid (pus) accumulates. Cavities can form in various parts of the upper and lower jaw.
There are 3 types of pathology:
- gingival (flux) occurs on the soft tissues of the mucosa, without affecting the periodontal ligament or teeth;
- periodontal – inflammation develops in the tooth root and periodontal pocket, which leads to mobility of the affected tooth;
- periapical – the infection spreads inside the pulpless tooth.
As for the symptoms of a tooth abscess, there are quite a lot of them, so the chance of detecting the disease in a timely manner is quite high.
At the onset of the disease, the patient may notice redness in the soft tissue area and slight swelling. Over time, swelling increases, causing soft tissue to swell in the jaw area, and this in turn leads to asymmetry of the facial contours. All this is accompanied by general malaise, weakness, loss of strength, loss of appetite, and problems with sleep.

An abscess is an infectious formation on the mucous surface, inside which pathological fluid accumulates
The affected tooth in the area of formation begins to ache and ache. Any meal causes severe discomfort, and when pressing on a tooth (biting, chewing), the patient feels a sharp pain. The sensitivity of the enamel to temperature factors, as well as to sour, sweet and spicy foods, also increases.
At the site of tissue redness, a cavity filled with pus forms and other pathological fluid. If the cavity spontaneously breaks out, an open ulcer appears in its place. All this is accompanied by a putrid odor from the mouth and a bitter taste.
During the period of active spread of infection, patients may also complain of high fever and swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck.
Sometimes it happens that some symptoms suddenly stop. As a rule, this indicates the death of the damaged tooth root. The disease will recur in a few days with renewed vigor, and during this time the infection can reach the jaw bone.
If the capsule opens on its own and there is an outflow of pus from its cavity, the patient may also feel an improvement. The pain will temporarily subside, swelling from the face and lymph nodes will subside, and general health will normalize. And at this moment it is very important not to give up treatment, but rather to promptly make an appointment with a dental surgeon.
Opening an abscess can transform the disease from acute to chronic, which will cause new outbreaks of the disease and symptoms. The chronic form is dangerous due to its frequent relapses and the appearance of the so-called “fistula tract”.
Treatment of illness using classical medicine
First of all, the doctor must make an accurate diagnosis, excluding other variants of diseases and pathologies. A visual examination of the oral cavity and the affected tooth is carried out, information about all symptoms is collected. A characteristic feature The appearance of an abscess is the presence of a cavity filled with pus.
In some cases, an additional x-ray is prescribed, which will help exclude other pathologies with similar symptoms.
One of the standard methods of treating this disease is surgical opening of the cavity and ensuring the outflow of pus.
Once the diagnosis is made, the dentist discusses a treatment plan with the patient aimed at preserving the tooth while eliminating the cavity followed by debridement.
One of the standard treatments for this disease is surgical opening cavities and ensuring the outflow of pus, after which the wound is treated with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Often the wound also needs to be drained. The dental surgeon performs a root canal, removing necrotic tissue from the area of the tooth root. After this, the doctor fills the damaged tooth.
If the infection has severely destroyed the tooth, then saving it is not advisable. The doctor removes the tooth (the main source of inflammatory processes) and may suggest installing a temporary crown - an implant. If a severely damaged tooth is preserved, there is a high chance of complications of the disease, the appearance of cysts and other formations, and the development of osteomyelitis.
In case of tooth amputation, it is also necessary to drain the capsule. The doctor performs the procedure through the hole left after removal.
Sometimes it is advisable to drain the cavity through an incision made near the capsule itself in the area of swollen soft tissue.
Laser opening of the capsule with subsequent drainage can also be considered a modern treatment option. High temperatures in laser beams coagulate blood vessels and produce a disinfecting and hemostatic effect. Healing after using a laser occurs much faster, and the procedure itself is less painful.
Drug treatment of the disease involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, painkillers, applications and oral baths. Conservative treatment in no case replaces surgical treatment.
Treatment of illness with traditional medicine

Severe pain, as well as swelling of tissues, can be removed with ice or cooled objects.
Many doctors allow treating a purulent tooth abscess at home. Application of methods traditional medicine will help slow down the inflammatory processes, however, this will serve as a temporary measure until you make an appointment with a specialist.
Severe pain, as well as swelling of the tissues, can be removed with ice or cooled objects. Apply a piece of ice wrapped in a cloth to the outside of your cheek or jaw where the infection develops. It is strictly forbidden to use a hot heating pad or compresses - this can only aggravate the process and accelerate the spread of inflammation.
Additionally, pain can be relieved with the help of anesthetics (Analgin, Nise, lidocaine solution, etc.).
General health can be improved with the help of antipyretic drugs, as well as drugs to reduce swelling.
You can also improve your health without using chemicals.

Rinsing with saline-soda solution helps with tooth abscess
- Rinse your mouth with warm saline-soda solution. You can also use herbal decoctions, propolis infusion, a drink with aloe juice or eucalyptus for rinsing.
- Apply compresses to the area. For this purpose, a potato mixture is used (grated potatoes are applied to the inflamed area and this mass is tied for 3-4 hours). Aloe compress is also effective. Cut the fleshy lith and apply the cut to the inflamed area. An onion compress will help speed up the maturation of the abscess (grate the vegetable or finely chop it, then apply directly to the abscess).
In case of an abscess, do not get carried away with self-medication and do not try to open the abscess yourself. If primary signs appear, promptly make an appointment with a doctor and strictly follow his instructions.
Dental granuloma is a small round inflammatory formation with clear boundaries.
It is located at the root of the tooth, mainly at its apex.
This is a rather dangerous disease, as it can lead to dangerous complications.
Causes of dental granuloma
Tooth root granuloma can be caused by:
- or inflammation of the tissue around the tooth;
- complication of pulpitis;
- tooth fracture;
- other injuries that may lead to infection;
- non-compliance with antiseptic rules in the treatment of other dental diseases.
An increased likelihood of developing more acute manifestations occurs when:
- stressful situations;
- sudden climate change;
- hypothermia;
- a previous cold;
- physical stress, etc.
Symptoms of dental granuloma
 Up to a certain point, the presence of a dental granuloma may be invisible to both the dentist and the patient. In the early stages, the disease can only be detected using radiography or orthopantomogram.
Up to a certain point, the presence of a dental granuloma may be invisible to both the dentist and the patient. In the early stages, the disease can only be detected using radiography or orthopantomogram.
The granuloma area then begins to grow. This occurs due to the fact that granular tissues take the place of cells killed by the inflammatory process. The growth occurs quite quickly and as it grows, pain and swelling of the gums comes.
At the next stage, suppuration of dental granuloma may develop. This causes severe pain, redness and swelling of the gums. The tooth darkens, purulent discharge appears between the tooth and the gum. All this can develop into odontogenic periostitis (flux) and will already be accompanied by a headache, high temperature, malaise, etc.
The disease can also be asymptomatic and develop into a jaw cyst.
Complications of dental granuloma
An unpleasant, but not the most catastrophic consequence of the complication is the loss of a tooth due to the destruction of its root. Further growth of tooth root granuloma can spread it to the surrounding soft tissues with the development of a purulent lesion there. Further spread of pus can cause osteomyelitis of the jaw, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, infectious myocarditis, as well as many other diseases and even death.
![]() Stomatitis is one of the most common diseases of the oral mucosa. Peculiarities .
Stomatitis is one of the most common diseases of the oral mucosa. Peculiarities .
When the first symptoms of the disease occur, it is necessary to limit the use of shared utensils, towels and other items. What else needs to be done when treating stomatitis at home, read the following.
Diagnosis of dental granuloma
![]() It is possible to recognize a dental granuloma only when symptoms of its growth and suppuration appear, since in the early stages of the disease the infected tooth appearance no different from healthy.
It is possible to recognize a dental granuloma only when symptoms of its growth and suppuration appear, since in the early stages of the disease the infected tooth appearance no different from healthy.
The final diagnosis is made after radiography. The image shows a limited, rounded dark area at the top of the tooth. Only in this way can it be distinguished from periodontitis and other diseases.
Dental granuloma can also be detected through radiovisiography.
On early stage Without the appearance of symptoms, dental granuloma is diagnosed extremely rarely.
Treatment of dental granuloma
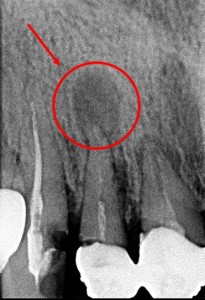
Photo of granuloma on the root of a tooth
At the first signs of the disease, you should consult a doctor, which some patients neglect, bringing on themselves serious complications. The treatment itself consists of removing the infection and preventing the possibility of recurrence.
Let's consider two options for treating granuloma on the tooth root:
surgical and therapeutic.
Therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma is carried out at a relatively early stage of the disease using sulfonamide drugs and antibiotics. Helps stop the development of the disease in time and get rid of the infection without a trace, as well as preserve the tooth or part of the tooth for its further prosthetics and restoration.
In particularly advanced cases, the dentist will not be able to do without surgical intervention. Previously, it was limited to tooth extraction. Currently, the doctor cuts the gum to drain the pus. Pus, if not removed in time, can enter the bloodstream through the soft tissues of the muscles of the face and neck and reach the heart, which in the worst case leads to the death of the patient.
To prevent the wound from closing prematurely, since in this case residual pus may remain in it, drainage is installed in the incision, for an average of three days. At this time, drug therapy is administered to relieve inflammation.
During surgical treatment, there is also a chance of saving the tooth or part of it, except in cases where:
- the disease initially arose due to a crack in the tooth;
- the tooth was so destroyed during the course of the disease that it cannot be restored;
- the source of the disease was the periodontal pocket;
- the patency of the root canals is impaired;
- the disease is caused by any other pronounced lesions of the tooth.
Self-treatment of dental granuloma
Attention! You should not self-medicate. Even if you know the names of antibiotics that are used for dental granuloma, any mistake in their use can be harmful to health and also lead to irreparable consequences.
Do not apply hot compresses to the area of inflammation. This will cause the pus to spread faster. Any attempts at self-treatment will only lead to a worsening of the patient’s condition. Leave the decision on treatment methods to specialists.
Treatment of dental granuloma folk remedies can also lead to disastrous consequences.
Prevention of dental granuloma
 Prevention of granuloma, like other dental diseases, consists of brushing them at least 2 times a day and visiting the dentist once every six months.
Prevention of granuloma, like other dental diseases, consists of brushing them at least 2 times a day and visiting the dentist once every six months.
In this case, you most likely will not develop a dental granuloma.
If you have any symptoms of gum or tooth disease, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Do not forget that pulpitis and periodontitis can develop into dental granuloma.
 When periodontal disease develops, it negatively affects teeth, leading to their deterioration and loss. Treatment of periodontal disease at home involves taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
When periodontal disease develops, it negatively affects teeth, leading to their deterioration and loss. Treatment of periodontal disease at home involves taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
Do you have swelling of your gums, lips or cheeks? presence of symptoms of periodontitis.
Accompanied by an accumulation of pus in the gum, this is a tooth abscess. Unfortunately, it does not heal on its own. The patient will need the help of an experienced dentist, after which the discomfort caused by the disease will disappear.
Causes of the disease
Among the causes of an abscess it is worth highlighting:
- a tooth disease that was not given much importance without starting treatment, as a result of which an abscess appeared at its root, for example, caries or periodontitis;
- trauma to the tooth, due to which it was either split or even broken, in which case the abscess occurs due to infection of the injured area;
- the disease can be caused by a complication after an ordinary sore throat or GRVI, since the infection is present in the entire bloodstream and spreads throughout the body, which is why they are called infectious; first of all, the complication can occur in people with weakened immune systems;
- purulent boils formed after inflammation of the hair follicle and localized in the jaw area (and therefore in close proximity to the teeth);
- infection due to unsuccessful treatment, for example, injections or after removal of nerves at the root of a tooth.
The process of the formation of an abscess on the root of a tooth is the same in all cases: the integrity of the enamel is disrupted, inflammation and the formation of an abscess. If treatment is not started by a dentist, the tooth abscess will become more complicated. Not only the tooth, but also the entire jaw can be damaged, which is caused, for example, by phlegmon of the oral cavity.
Picking your teeth with dirty hands can cause an infection.
How to identify an abscess?
The disease has several characteristic symptoms:
- constant sharp pain in the area of the infected tooth, sometimes throbbing, sometimes aching;
- redness of the gums and swelling (even an open purulent ulcer may form), as well as swelling in the soft tissues of the jaw;
- pain when chewing;
- unpleasant sensation after very hot or cold food or drinks;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes, accompanied by their enlargement;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- general malaise.
Complications from an abscess
Sometimes symptoms disappear, but you should not assume that everything is fine. A dental abscess does not go away on its own. Most likely, this is the death of the tooth root. But the infection remains and continues its path deeper and deeper into the tooth tissue, and closer and closer to the jaw bone. An abscess can develop into a chronic one when it forms. Most often this happens after an attempt to remove the abscess on your own or when it opens on its own.
Among the diseases that threaten a careless patient:
- brain inflammation;
- inflammation of the bone marrow;
- pneumonia;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- sepsis;
- diabetes.
Some of them can be fatal, others are chronic and require constant treatment with expensive drugs. A trip to the dentist to remove an abscess at the root will cost less.
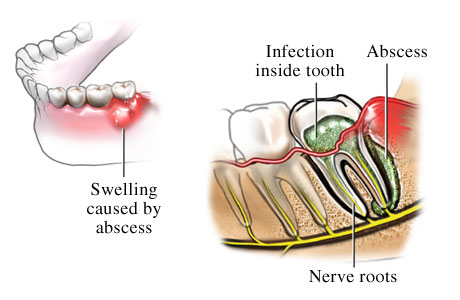
Treatment of tooth abscess
There are several treatments for this disease. Very often they are combined to make it effective and to achieve the main thing - tooth preservation. Let's look at the most common of them.
Drainage
Drainage of the abscess and disinfection of the affected area at the root.
Canal treatment
The infected pulp of the tooth is removed and the abscess is opened, pumping out the pus. After this, the dental canals are filled and sealed. All this is topped with a crown.
If there is simply nothing to put a denture on after removing the pulp, you will be recommended surgery. So, to install the prosthesis, neighboring tissues are used, but this should in no case harm them. Therefore, in such a difficult case, it is worth contacting a professional, even if it costs more.
Removing an infected tooth
Dentists resort to this method in extreme cases, if canal treatment cannot be limited to. Of course, this is far from a pleasant procedure, akin to surgery. After all, the tooth is not only removed, but also all affected tissue is scraped out in order to stop the infection from spreading deeper. Thus, in place of the damaged tooth there will be nothing, only a recess.
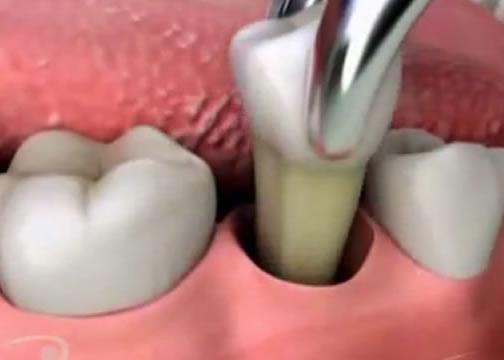
Surgery
This is generally the most extreme method of treatment when a dental abscess is so advanced that it has spread to the mouth, jaws and neck of the sick person. The operation, of course, is performed under anesthesia. This should stop the infection, but if this still does not happen, the doctor will prescribe additional examinations, including a biopsy, to finally establish the cause of the disease and eliminate it.
Treatment with antibiotics
Often used after removing an abscess to prevent the infection from spreading. will help the body destroy harmful microorganisms that caused the abscess. After just two days of treatment with them, the symptoms weaken, and after five days the disease should pass.
But antibiotics are prescribed only after ultrasound confirmation that you really have this disease, because these drugs have many contraindications and have a detrimental effect on the microflora of the body’s mucosa. Therefore, when treating them, it is better to also take medications for the intestines containing bifidobacteria in parallel.
Rinse
Rinsing with brewed oak bark or water and salt may be prescribed. You should rinse your mouth as often as possible if you suspect you have an abscess, but have not yet had time to see a doctor or are waiting for your appointment. Thus, the pus along with negative microorganisms will be rinsed out of the mouth.
Dentists also prescribe rinsing to ensure that the tooth heals well, without discomfort for the patient, and the affected area recovers more quickly.

Taking painkillers
Medicines such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and others will help eliminate pain and discomfort, reduce the temperature, but will not cure. This is a temporary method; doctors use it after removing the abscess, if the patient is physically unable to bear the pain. Especially in cases where it is not possible to take a day off or sick leave during recovery.
To never find out what a tooth abscess is, take care of yourself: try not to get too cold, brush your teeth every day, and most importantly, contact your dentist on time.



















