How to start trading shares on the stock market. How to start trading shares on the stock market.
There is a strong opinion that trading shares for novice traders on stock exchanges without a mentor is risky and obviously unprofitable. This happens, but only among those beginners who take Internet trading lightly and do not delve into the basic principles of securities trading. What should a novice trader know?
Which exchange to settle on?
The choice of Russian exchanges for stock trading is quite modest - only two platforms: MICEX and FORTS. Trading in shares mainly takes place on the MICEX, and it’s worth settling there to begin with.
The principle of operation of exchanges is quite simple: sellers and buyers place orders to buy and sell shares in in electronic format and send them to the exchange's computer system. The system automatically compares and analyzes applications, and then closes transactions with similar conditions. After the transaction, the shares become the property of the buyer.
Why do we need brokers, and how to choose them?
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, a private person cannot independently trade securities on the stock exchange. The purchase and sale of shares can only be carried out by a legally registered person who has a special license. Such legal entities are brokers - intermediaries between the client and the stock exchange. Brokerage firms charge a certain percentage for their services.
When choosing an intermediary, you must adhere to the following principles:
- Give preference to well-known companies with a positive reputation and good reviews from clients (reviews of the work can be found on thematic forums).
- Check for a license to work with stock exchanges.
- Choose a broker that provides the opportunity to work via the Internet. Study the program for accessing the exchange, its ease of use and cost.
- Check the amount of commissions for each transaction, the amount for servicing and maintaining accounts, as well as guarantees for the reliability of the system.
- Find out how you can replenish your account and withdraw money from it.
Responsible brokers provide the client with a training program for working on the stock exchange and the opportunity to practice on a virtual account.
Exchange strategies
Trading on the stock market without a strategy is a direct path to losses and disappointments, however, there are no 100% winning strategies. Market analysis, intuition and experience will eventually allow you to develop your own trading system, and at the beginning of your journey you can use one of the classic methods:
1. Follow the trend - buy shares during growth periods and sell them at the peak of activity at a higher cost.
2. Invest - conduct an economic analysis of the market and buy shares of companies that will grow steadily in the future in order to receive dividends from them.
3. Use a system of patterns - focus on the patterns of exchange trading and price changes, making transactions based on their analysis.
4. Control-trend system - consists of buying shares when their prices are declining, expecting further growth. This system is one of the riskiest, so it should be used with extreme caution.
5. Trading based on news - when purchasing, the main economic changes in the country and within companies are taken into account, and the reaction to these changes in the securities market is calculated.
How to start trading?
In order to start trading shares, you need to choose a reliable dealing center and register there. Through the center's program, open an account on the exchange and deposit money. Download the trading terminal provided by the dealing center and the training program onto your computer. After completing the training, you can immediately start trading or continue training with a virtual account.
Secrets of stock trading - do they exist?
There are no magic recipes that guarantee the success of a trader on the stock exchange. However, there are a few important rules, the implementation of which will significantly increase the chances of stable successful trading:
- Take your time and avoid spontaneous actions - it is better to miss one or two successful transactions than to waste all your money.
- Try not to use the broker's borrowed funds (leverage) in a ratio greater than 1:50.
- Choose a simple strategy and explore its capabilities in different situations.
We have described only the main points of how to start trading shares. Be prepared for the fact that you will have to study a lot, because ignorance of some nuances can seriously hinder your success in this field.
The Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange (MICEX) has existed since 1992. In 2012, it was merged with RTS and renamed Moscow Exchange OJSC.
Almost immediately, the updated MICEX became the best Russian stock exchange, both in terms of the number of clients working on it and in terms of trading volume. Today the Moscow Exchange is one of the twenty largest in the world.
The principle of operation of the Moscow Exchange
The Moscow Exchange carries out transactions with currencies, securities, shares of exchange-traded funds, futures, options, precious metals and other financial instruments. Clients of the trading platform - credit institutions, management companies, non-governmental pension funds, exchange intermediaries, institutional and private investors who work on the exchange through intermediary brokers. The main work at the Moscow Exchange is concentrated in data centers, where powerful equipment and special software necessary for conducting and recording exchange transactions are installed. Investors send applications for transactions through trading terminals that are connected to the Internet. All information received from users is recorded in the exchange database.
The Moscow Exchange pays special attention to security. It is impossible that personal data will be stolen or lost: every transaction carried out in the system is verified electronic signature investor.
How can a beginner start trading on the Moscow Exchange?
There is nothing complicated about starting to trade on the Moscow Stock Exchange. To gain access to the Moscow Exchange, you need to perform a number of simple operations:
- Find a suitable broker. The domestic securities market is structured in such a way that individuals cannot trade on the exchange directly. Therefore, all stock exchange transactions on behalf of private investors are carried out by stock brokers. Finding an intermediary is where you should start trading on the Moscow Exchange. The general list of trading participants is presented on the exchange website.
- Select a tariff. You need to start working on the stock exchange by choosing a tariff plan from a broker. To do this, soberly assess the volume of transactions you plan to make. Traders who do not carry out too many transactions on the exchange will benefit from tariff plans with a fixed minimum fee for brokerage services. Active investors should compare rates to see what fees are charged based on the volume of trades made over a given period: generally, the higher the volume of trades, the lower the transaction fees.
- Conclude a service agreement with the broker. There are two ways to do this: without leaving home, open an account remotely through the government services portal or personally come to the office of a brokerage company. When visiting in person, you must have a set of documents with you, a list of which can be found on the official website of the intermediary. After the conclusion of the agreement, a brokerage account will be opened in the name of the applicant.
- Select a trading terminal. To start trading on the Moscow Exchange, you need suitable software. Each broker offers its own version of a trading terminal, sometimes even of its own design. The list of the most popular ones includes QUIK and MetaTrader 5.
- Set up the software. For settings software We recommend watching a video course on working in the QUIK program or a video course on Metatrader 5.
- Deposit funds into the account. Even for “dummies” it is no secret that it is impossible to trade on the Moscow Exchange without money. Therefore, before you start real trading, deposit some money into your account. This can be done either through the bank’s cash desk or through numerous online services. It should be remembered that the money in the account is not insured, so the trader takes full responsibility for incorrect transactions. Therefore, before you start trading on the stock exchange, you should thoroughly study all the intricacies.
How is trading conducted on the Moscow Exchange?
There are three main markets on the Moscow Exchange, and each of them has its own operating schedule.
The stock section of the Moscow Exchange is the base platform where you can invest in Russian or foreign assets. This section is available to both residents of the Russian Federation and residents of other countries.
The start time of trading on the main market of the Moscow Exchange is 10:00 (MSK), the pre-trading period starts at 09:45.
Main trading takes place from 10:00 to 18:40 (MSK).
On the currency section of the Moscow Exchange, Swiss francs, US dollars, pounds sterling, euros, Chinese yuan and Hong Kong dollars are traded in two delivery modes - TOD (for today) and TOM (for tomorrow). All currencies are traded against the ruble.
Trading time on the currency section with TOD delivery mode:
US dollars - from 10:00 to 17:15 (MSK)
Swiss francs, pounds sterling, euros - from 10:00 to 15:15 (MSK)
Chinese yuan and Hong Kong dollars - from 10:00 to 10:45 (MSK)
Trading hours on the currency section with TOM delivery mode for all currencies - from 10:00 to 23:50 (MSK)
The derivatives section of the Moscow Exchange is the territory of futures and options contracts. The list of the most popular assets includes the RTS index, currencies different countries, oil, gold, raw materials.
The pre-trading period on the derivatives market starts at 9:45 am. Trading begins at 10:00 and continues until 23:50 (MSK).
With more detailed information The trading schedule can be found on the Moscow Exchange website.
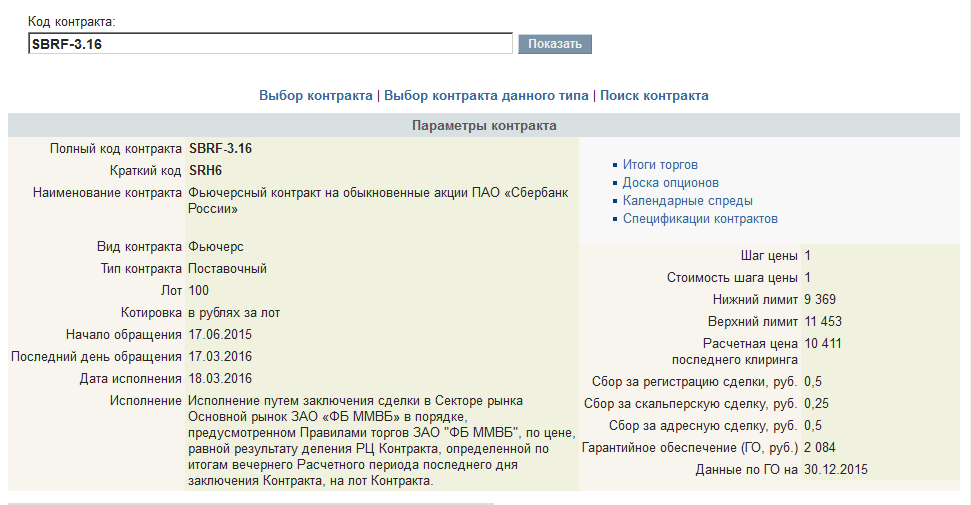
Futures specificationOn the exchange website you can see all the parameters of the futures in its specifications. Specifications of all derivatives contracts - http://moex.com/ru/derivatives/contracts.aspx?p=act
1.
To find the contract we need, we must know its code. The code can be complete or short. Let's look at the example of futures for ordinary shares of Sberbank. (“Ordinary” shares are called as opposed to preferred shares. The difference is in the right of access to the management of the company and the procedure for calculating dividends.)The letter designations of the months can be studied at these two links:
2.
We are interested in futures exclusively as a tool for speculative trading, that is, trading that generates income from differences in prices over different periods of time. We will not go out for delivery of the underlying asset on a futures contract, so let’s look at the lifespan of this instrument. Futures begin trading approximately a year (sometimes more) before their expiration date.Expiration is the last day of futures trading. The day on which trading on it ceases and settlements (or delivery) are made between the remaining participants in the transactions. The expiration date is known in advance and usually falls in the middle of the calendar month.
Futures are either settlement or delivery. Settlement futures are those for which, on the expiration date, all settlements between participants are made exclusively in money. Delivery - provide an opportunity to supply a specific product (stocks, raw materials, currency). This parameter is also indicated in the specification:
Very often, beginners are interested in the question: what will happen if I forget to sell the purchased futures by the expiration date? Will they deliver a barrel of oil or a bag of shares to my door? Unfortunately, no, you won't have that kind of fun. On the eve of expiration day (or even a few days before), the broker
will send a warning about the approaching expiration date directly in the messages of the trading terminal through which you make transactions. And, if this warning does not affect you, then he will close your position (that is, buy or sell your open position) at the agreed time
broker rules time. There are no penalties for forced closure, although increased fees may apply. If you deliberately want to receive its underlying asset after the end of the futures circulation, then you must notify your broker about this in advance.3.
The expiration date, as well as the contract circulation start date, are also indicated in the futures specification. In addition to them, the execution date is indicated - the day on which settlements are made for the delivery and final payment of those contracts that were deliberately brought to expiration by trading participants.
4.
As I said earlier, a futures is a contract for the delivery of a certain amount of an underlying asset. In our case, ordinary shares of Sberbank are traded on the stock exchange in lots of 10 pieces. A futures contract is for a larger number of shares. This is also indicated in the specification. This parameter is also called “lot”. For ordinary shares of Sberbank it is equal to 100 shares.Futures contracts for different stocks may contain different numbers of shares in a lot (from 10 to 100 thousand pieces) depending on the price of one share. Thus, the futures price will correlate with the price of one share multiplied by the number of shares in the lot.
5.
When buying or selling a futures contract, the trader does not pay the full price, but only a small part, which is called the margin. GO is calculated daily by the exchange and indicated in the specification. At the time of writing this text, GO
futures for ordinary shares of Sberbank were set at 2,084 rubles. On some days, the GO may be significantly increased - on days before and after long holidays, on days with increased price volatility due to the news background.6.
Also, based on the results of the trading session, the Settlement Price and the upper and lower limits for each futures are calculated daily.The settlement price is calculated using a special method, taking into account the prices of the latest transactions and active orders in the trading session. It is used to determine the amount of guarantee security.
Upper and lower limits are price limits upon reaching which trading will be forcibly stopped. This is done to prevent uncontrollable sharp and unexpected price jumps with which the market may react to any strong news. The slang name for these limits is “bar”.
7.
In addition to all of the above, the specification contains the size of the commission per transaction and the price step and cost of the price step.A transaction, unlike Forex, on the exchange is considered one transaction, that is, a purchase OR sale. Suppose you make a purchase (enter a position) - this is one transaction. Exiting a position (or closing it) is done by an opposite transaction, that is, a sale - and this will be another transaction. The total commission for opening and closing a transaction is called the “circle” commission. The commission specified in the specification is taken from one contract, but if you enter a large number of contracts, then the commission must be multiplied by the appropriate number.
Let's figure out what they mean different types transactions indicated on the screen:
A targeted transaction is a transaction indicating a specific counterparty with whom you have agreed on it in advance. Commission size - 0.5 rub. (On a circle
for one contract - 1 rub.) All other transactions on the exchange are addressless.A scalping transaction is a transaction completed within one trading session. That is, if you opened and closed a position within one trading day without transferring it overnight. Commission size - 0.25 rub.
For all other transactions, regardless of the number of days during which you held the position, a commission of 0.5 rubles is charged.8.
The price step and the cost of the price step for the instruments that I trade is 1. That is, the minimum price can change by 1 point, the cost of which is 1 ruble.
A general view of the futures specification is shown below:
As soon as an investor or a novice trader thinks about what to do with his savings, he inevitably faces the question: “Where to start?”
In fact, you shouldn’t put money in the bank at ridiculous interest rates. Moreover, you won’t receive this interest later. If we also take into account the very real prospect of losing the entire amount in the same bank, then the benefits of such a management of money become quite obvious. Approximately these thoughts tormented the author when he thought about the unenviable fate of investors who entrust their money to all sorts of scammers. This was probably the impetus for going thorny path exchange player. Naturally, first of all, the author was faced with the same question - "Where to begin?".
Stock trading for beginners
The simplicity of the question touched me, but it didn’t make it any easier. It is not worth reproducing here the entire path that the author had to go through before he understood what needed to be done when the intention to trade on stock markets arose.
Having many mistakes behind him, made solely due to a lack of experience and knowledge, he decided to present here his main considerations about where, in fact, one should start. So, the first question to be solved looks quite simple.
1 It goes something like this: “What markets will I trade in?”
But this question seems simple only at first glance. In fact, it is fraught with danger, because without paying proper attention to it, you can very realistically find yourself in a dead end. The thing is that every market has its own characteristics. At the same time, they inevitably give rise to certain “pros” and “cons,” which, in turn, have more or less weight for each individual person, depending on his personal preferences.
To make it easier to understand this issue, we will try to consider all its components in order. This will allow you to organize your thoughts into a system. First of all, you should find out geographical position trade. In other words, in which market, by territorial basis, will trading operations most likely be conducted? For Russian investors and traders, there are basically three such points: Russia, Europe, and the USA.
Some, however, may turn to other markets - Australia, India, Asia in general, etc. - but still it’s rather exotic. In each case, the procedure is almost the same: you need to choose a brokerage firm, open an account, and then you can trade, not forgetting, of course, to transfer money in a timely manner. But this should not be done first, but at least only after you read this article.
The second problem is related to the first and may require you to rethink a previously made decision. The problem is figuring out what to trade. This question is not idle. The Bloomberg news agency reported in early 2000 that it broadcast market data on approximately 2.5 million financial products. To view all this data, spending only one second on each product, will require exactly a month of continuous work. It is unlikely that anyone will want to experience such pleasure for themselves.
In reality, to solve this problem they turn to the so-called “market segmentation”. Speaking in simple words, each type of financial instrument belongs to a specific segment. There is a property market (equity). The most active market here is the corporate stock market. There is also a bond market, which is usually divided into the market for corporate bonds and government debt securities.
Also considered the most famous is the commodity futures market (commodity), where transactions are made on futures not only for commodities, but also for currencies and indices. And finally, we should mention the market for cash foreign exchange transactions - the Forex market. There are others, smaller ones, but in this case it's not that important.
How to understand all this and what to give preference to? Usually this is a personal matter for everyone, so it is extremely difficult to advise here. Typically, investors and traders concerned about their capital prefer the stock and futures markets. Some people are drawn to currency trading. Here you need to pay attention to one circumstance: the selected market segment is very closely related to which territory you prefer to trade.
If you are planning to trade futures, then in Russia you are unlikely to have anywhere to turn around, unless you are going to specialize in one or two financial instruments. The most developed futures market right now is America, where you can even find temperature trading contracts. The same can be said about the stock market.
Once you have at least tentatively decided what to trade, you should think about how to obtain data from the market and how much it will cost. The question is important, and in no case should it be discounted, since it can easily affect the previously made decision. To make it clear what we are talking about, imagine this picture.
You intend to trade on the European stock market. How many information sources can you find? How many programs can you find that can be considered as alternative options? In any case, a lot of effort will be spent. At the same time, there is more than enough information about the American market - it’s not even easy to hide from it!
Accordingly, the most comprehensive offer is of software products that provide analysis of the American market specifically across the entire range of financial instruments. The same can be said about data providers. This is an important point, since the choice of an acceptable amount of inevitable costs depends on it. In addition, ordinary investors and traders now usually use the Internet to connect to the data flow. As practice shows, it is easier to obtain data from America than from neighboring Germany.
Now it’s time to think about why, in fact, all this is being done. A question with an obvious trick. Ninety-five percent of traders, and perhaps more, answer it something like this: “To make money.” Unfortunately, this answer is incorrect. If we start with such reasoning, then it is indeed better to take the money to the bank, even with dubious prospects of getting it back. After all, monetary losses become almost inevitable in this case. The correct answers may sound something like this: “to successfully invest money”, “to improve the management of your own funds”, “to receive additional income in exchange for some risk”, etc. The difference in the answers obviously seems quite insignificant to you. In fact, it is huge. To understand this, you should turn to a solution to such a problem as market analysis.
Thus, in the next step, you need to understand the principles of conducting market analysis. Currently, there are many theories and a wide variety of opinions on this matter. One of the most common methods is technical analysis. What it is? This approach is based on the assumption that the use of various indicators, as well as the study of price bar configurations, will help in predicting the market situation in the future. Proponents of fundamental analysis call this a fallacy and are of the opinion that by studying the economic environment, more significant results can be achieved.
In practice, both of them turn out to be idealists, because neither approach guarantees complete success and is not able to protect against serious mistakes. The only way is to combine both approaches through your own common sense. When studying how to conduct market research that precedes fundamental decisions for a trader, you should turn to publications that are devoted specifically to this topic - technical and fundamental analysis. Now the reader can familiarize himself with such an extremely useful magazine as “Technical Analysis: Stocks & Futures”.
As you learn the basics of analysis, a rethinking of the market usually occurs. This leads to the need to reconsider our understanding of the tools that are used in analysis. Having penetrated deeper into the specifics of market analysis, you may realize that you need a completely different software product that provides analysis. Even if such a feeling does not arise, at this stage it is still recommended to reflect on the question: “How to conduct market analysis?” In other words, which technical analysis package should you choose?
At this stage, you should at least first decide what type of trading operations you intend to carry out. This is extremely important question, since there are four main alternatives: day trading (trading a large number of securities with fixation of small amounts of exchange rate changes within 1/8 or so), intraday trading (involves opening and closing trading positions within the trading day), short-term trading (Short -Term, - usually understood as a trade lasting several days), and, finally, Long-Term trade (Long-Term - this usually refers to trade that lasts from 30-40 days). As you understand, the choice of the above-mentioned types of trading depends on your preferred investment horizons.
And only now we have to decide the question: “Which broker should I trade with?” It is clear that the choice of a broker and the conditions he offers depends on the type of trading behavior. If you intend to day trade, you should contact a firm that provides direct access to the “trading space”. Short-term trading is not so demanding; here you can limit yourself to a regular online broker. For long-term trading, a phone is often enough. Of course, all this should not be taken as dogma, but it should still be taken as a basis. Commission; the quality of the software product that allows entering orders into the system (if this is not done through a Web browser); reliability of connection with the broker's server; the speed and quality of execution of entered orders - all these are very important little things that should be carefully weighed before giving preference to one or another company. And here it doesn’t hurt to find out through which clearing company the brokerage firm you are interested in works through, how client orders are routed, and what are the reviews about this firm. The resources of the NASDAQ website provide coordinates by which you can find out, for example, whether there have been negative moments in the history of a particular company. And it is highly recommended to do this! Sometimes it is also important how wide the range of financial instruments that can be traded is. This is especially true for the commodity futures market.
We just need to remind you: the industry of providing services in the stock and futures markets in the United States and in a number of developed countries of the world operates so steadily and is so tightly controlled that many brokerage firms simply would not think of drawing up two copies of the contract. This may seem like a scam to some, but as one investment manager once popularly said, “It’s much harder to steal here than at the bank.” That is why a brokerage service agreement is a public offer agreement in the form of a unilateral agreement. It's similar to the deal you make when you buy a magazine: by handing over the money, you've essentially agreed to the terms opposite side. In the case of a broker, consent is expressed by the presence of your signature. So if you want to have a contract in your desk drawer, be sure to make a copy before sending a copy to the brokerage firm. If the matter concerns an American or British company, this is even more necessary.
When the choice is made, there is nothing left to do but rush into the abyss of the stock market. True, the most meticulous and cautious investors will not rush, but will work on drawing up rules for portfolio management. In any case, “fundamentalists” (those who adhere to fundamental analysis) devote a lot of time to this. Ardent supporters of technical analysis are engaged in the design and testing of trading systems. In opposite positions are those who worship the science of money management. They tend to view everything through the prism of probabilistic processes and statistical series, or operate with mathematical formulas that allow them to calculate all the necessary parameters for risk and profitability. Be that as it may, in reality, no type of trading approach can guarantee 100 percent success. The market simply does not tolerate certainty; it immediately rejects any certainty. Watching a bullfight will help you understand this. How will a bull behave in the arena when a red rag is waved in front of its very nose?
You should never forget that everything in this world changes. What seemed worthy of respect to you yesterday may no longer be taken seriously the next day. Then you will definitely reconsider your views on the market, perhaps even change the rhythm of trading. This is why investors and traders constantly “wander” from one broker to another. It is for this reason that the answer to the question of who to trade through should not be treated as an unshakable and unchangeable ultimate truth. Remember: everything in the world changes, and so does the market! Therefore, we must change with it if we want to trade successfully!
Individuals were given the opportunity to trade on the MICEX in 2012. At the same time, it was merged with the RTS and renamed the Moscow Exchange. Here you can make transactions with currencies, securities and derivatives. To start trading on Moscow Exchange, you need to complete a number of simple operations.
Transactions are possible only after opening a brokerage account. When choosing an intermediary, pay attention to the rating of brokerage companies. An independent assessment by traders is carried out on the website www.brokers-rating.ru. To ensure representativeness of the results, a limit on the number of votes per day is imposed on each user. After choosing a broker, you need to decide on a technological solution for trading. The Moscow Exchange has its own developments. These are trading terminals RTS Stocks and MICEX Trade Commodity. A special document has been released to track online trading. mobile app iMicex. It can be installed on a smartphone running Apple or Android OS.
- Get advice from a broker or exchange support specialist and choose a connection scheme.
- Decide on the connection protocol. This could be API or FIX/FAST.
- Organize a connection channel with the help of a provider.
- Test the terminal and troubleshoot problems if they occur.
- Carry out the certification procedure and receive keys for bidding.
With the terminal installed, you can start full-fledged trading on the Moscow Exchange. Please note that to conduct daily trading you must have at least minimal financial knowledge. If you doubt your abilities, start by working on the simulator.