Heavy bleeding on the first day of menstruation. Symptoms and signs. Video about the causes of pathology
Menstruation is a natural process that occurs monthly in the body of every woman of reproductive age in the absence of pregnancy. It does not pose any threat to life or health. However, this process is natural only if it does not involve bleeding. It is not surprising that these concepts are often confused, because they sometimes have similar symptoms. This is where the danger lies.
The fact is that bleeding is caused by some pathology. Therefore, if you do not seek medical help in time, you may experience undesirable consequences. In some cases, bleeding is fatal. Therefore, you need to know how to distinguish periods from bleeding.

If your periods have always been not too intense and suddenly become heavy, then this should not be ignored. It is possible that this is not menstruation, but uterine bleeding, therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to distinguish menstruation from hemorrhage
Since bleeding is a symptom of pathology, it should not be confused with menstruation. To do this, you need to know how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding. This can be done if you take good care of your body. Hemorrhage can be determined by the following symptoms:
- Copious bleeding. You can tell by changing the gaskets. When bleeding occurs every hour to an hour and a half.
- The duration of bleeding exceeds 8 days.
- The blood comes with a lot of clots.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle occur.
- Severe pain appears in the lower abdomen and lower back.
- Weakness occurs and health worsens.
- Bleeding occurs after menopause.
- The epidermis becomes pale.
- Blood flows after intimacy.
- Anemia develops.
- Bleeding occurs between periods.
- Hair begins to fall out a lot, and nails peel and constantly break.
If bleeding symptoms occur, consult a doctor immediately.
Implantation bleeding
 Periodic and abnormal bleeding is often confused with implantation bleeding. IN this issue You should also be well versed and understand how they differ. To do this, you need to know what each type of hemorrhage is, as well as the characteristics of each of these processes. Thus, implantation bleeding occurs after ovulation, when the fertilized egg attaches to the upper layer of the epidermis of the uterus, that is, after pregnancy occurs. During this process, the vessels of the uterus may be injured, resulting in the release of a small amount of blood.
Periodic and abnormal bleeding is often confused with implantation bleeding. IN this issue You should also be well versed and understand how they differ. To do this, you need to know what each type of hemorrhage is, as well as the characteristics of each of these processes. Thus, implantation bleeding occurs after ovulation, when the fertilized egg attaches to the upper layer of the epidermis of the uterus, that is, after pregnancy occurs. During this process, the vessels of the uterus may be injured, resulting in the release of a small amount of blood.
Implantation bleeding is the first sign of pregnancy. It usually occurs a week before the start of menstruation. Therefore, menstruation is often confused with implantation.
What is the difference between menstruation and implantation bleeding?
These processes can be identified by the following characteristic features:
- The duration of implantation bleeding is several hours, maximum days. If the discharge lasts longer, then you need to consult a doctor.
- With implantation bleeding, unlike menstruation, you may experience slight discharge. It could only be droplets of blood.
- During implantation bleeding, the color of the discharge is pink, red-brown and, one way or another, different from the color of blood during normal menstruation.
- During implantation, a decrease in basal temperature is observed. This is the main symptom of such bleeding.
Bleeding after childbirth
 Bleeding after childbirth is another type of hemorrhage that requires attention. During this period, suckers emerge from the uterus. Hemorrhages after childbirth cannot be confused with menstruation, because... There are no periods in the first 2 months after the baby is born. This applies to both natural and artificial childbirth. However, they can easily be mistaken for bleeding, and this is the main danger for a woman. Uterine hemorrhage leads to large loss of blood, which is dangerous for the body and can even be fatal. To prevent this from happening, you need to know in which cases bleeding occurs after childbirth, and in which cases we are talking about pathological bleeding. Understand what is needed medical assistance, based on the following symptoms:
Bleeding after childbirth is another type of hemorrhage that requires attention. During this period, suckers emerge from the uterus. Hemorrhages after childbirth cannot be confused with menstruation, because... There are no periods in the first 2 months after the baby is born. This applies to both natural and artificial childbirth. However, they can easily be mistaken for bleeding, and this is the main danger for a woman. Uterine hemorrhage leads to large loss of blood, which is dangerous for the body and can even be fatal. To prevent this from happening, you need to know in which cases bleeding occurs after childbirth, and in which cases we are talking about pathological bleeding. Understand what is needed medical assistance, based on the following symptoms:
- If the bleeding remains scarlet even on the sixth day after birth. The normal color of bleeding can be seen in numerous photos on the Internet.
- There is a fever, which is accompanied by chills.
- The gasket needs to be replaced every hour and a half.
- The blood comes out with a lot of clots.
- Bleeding continues for more than two months after birth and at the end of the period the blood turns scarlet again.
- Blood has bad smell, uncharacteristic of the smell of discharge during menstruation.
Even if there are no these symptoms, but the woman’s condition worsens after childbirth, she should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
How to stop bleeding
Only a doctor can stop the bleeding. It is not recommended to take any action on your own, because... this may make the condition worse. However, if the doctor has diagnosed normal heavy bleeding during menstruation, then this process can be stopped at home. IN in this case The following measures will help:
- Drink plenty of fluids, with the exception of alcohol and coffee. Such drinks should be excluded from the diet.
- No excessive physical activity.
- Exception water procedures during hemorrhages, as well as refusal to visit the steam room and sauna.
If there is pathological uterine bleeding, then cold will help stop it, or rather, not stop it, but reduce its intensity. To do this, a heating pad with ice or another cold object is placed on the woman’s lower stomach. After this they call ambulance.
Treatment of abnormal bleeding
Treatment of bleeding is carried out in a hospital by an experienced doctor. The first thing he must do is stop the bleeding. After this, you need to begin eliminating the cause that provoked this process.
Bleeding can be stopped using special medications. Along with their administration, the doctor may prescribe hormonal drugs. The fact is that hemorrhage often occurs due to hormonal imbalance. If the hormone levels are brought back to normal, the bleeding may stop.
In the event that bleeding occurs due to diseases of the uterus, abortion, etc., then it can be stopped by cleaning. This procedure helps to determine the cause of bleeding and eliminate it.
If bleeding occurs during pregnancy, the doctor most often prescribes magnesium. It helps not only stop bleeding, but also helps maintain pregnancy.
After the hemorrhage has stopped, it is necessary to replace the blood loss. Next, you should begin general therapy. In this case, you can take iron-containing medications, vitamins, etc. They are prescribed by their attending physician.
Every woman should be able to distinguish menstruation from other types of bleeding, because this will help maintain her health and possibly save her life.
Menstruation is a physiological process. With the regularity of the ovarian cycle, a woman’s body prepares to receive a fertilized egg. This is achieved by hormones that stimulate the growth of the inner layer of the uterus, where the fertilized egg should attach.
If pregnancy does not happen, everything is not in demand " construction material" is excreted from the woman's body. This is the basis for regular bleeding. Normally, monthly blood loss averages from 50 to 100 ml and does not lead to negative effects and symptoms.
Discharge during menstruation is fundamentally different from bleeding itself. They include mucus, endometrial cells and tissues, fermented, altered blood resulting from the physiological exfoliation of the “old” endometrium. It has a dark color and clots.
In terms of intensity, menstruation can be abundant or scanty. This depends on various factors:
- Individual characteristics, heredity.
- Climate, nationality.
- Overweight or, conversely, underweight.
- Labile (unstable) psyche.
- Age.
In any case, if in doubt and it is unclear how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding, it is better to consult a specialist.
Uterine bleeding
Uterine bleeding is a pathological process caused by various reasons, leading to blood loss and anemia of varying severity. How to distinguish bleeding from menstruation, consider the differences:
- An increase in the volume of blood loss during menstruation, compared with their previously normal course.
- Increased duration of menstrual flow.
- Failure of cyclicity (bloody discharge begins earlier or later than expected).
- Bloody discharge appears after sexual contact.
- Uterine bleeding after menopause during menopause.
How can you tell if it's heavy periods or bleeding? According to the following characteristics:
- Heavy discharge requires more frequent use of hygiene products, replacement every 1–2 hours.
- The amount of blood released is higher than usual.
- The color of the blood is brighter and red than during normal periods.
- General malaise, weakness, dizziness - not as usual during menstruation.
- The interval between menstruation is less than 20 days.
- General and biochemical blood tests show signs of iron deficiency anemia.
Types and classification

In each time period of a woman’s life, from her birth, the formation of the body occurs, its preparation for childbearing function, for pregnancy and childbirth, with its subsequent decline during menopause. This is the work of the endocrine glands and if a malfunction occurs, uterine bleeding can appear at any age:
- Blood discharge in newborns - for the first time days after birth, in the first week of life - is normal, goes away on its own, the cause is hormonal.
- Before puberty - false puberty: bloody discharge associated with hormonal tumor formations of the ovaries.
- During puberty - juvenile, caused by hormonal imbalances, emotional state, physical activity. Associated with ovulation disorders, more often with its absence. During puberty, it can be caused by pathologies: ovarian tumors, clotting factors, etc.
- In reproductive age - dysfunctional (ovulatory), organic, associated with pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth.
- During menopause, they depend on hormonal imbalance and diseases of the internal genital organs.
Bleeding during the reproductive period

During childbearing, the most important period in a woman’s life, the problem of how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding arises most often. At this time, there are many reasons for the manifestation of pathological symptoms. How do you know when to sound the alarm?
The main reasons in this age period:
- Abortions, spontaneous miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies.
- Bubble drift.
- Inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs.
- Gynecological pathologies (endometritis, endometriosis, hormone-dependent tumors).
- Blood loss during and after childbirth.
- Dysfunctional disorders.
Implantation bleeding is a small amount of bloody discharge at the time of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium of the uterus. This slight discharge lasting several hours often goes unnoticed due to its scarcity.
During pregnancy, bleeding is associated with its interruption early stages, with the development of an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy.
In the second half of the term, blood loss is sometimes caused by serious pathology - placental abruption, uterine rupture. In such cases, pregnant women with signs of bleeding are observed in the hospital.
Dysfunctional blood loss
Associated with hormonal imbalances, stress, poor diet and other health disorders, but are not accompanied by persistent pathological changes that lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle. There are:
- Ovulatory (in the presence of ovulation) - in women of childbearing age.
- Anovulatory (in the absence of ovulation) - during puberty and during menopause.
Organic uterine blood loss
Accompany diseases of the female genital area. It can be confused with menstruation if the pathology that caused the bleeding is chronic and does not have a clear clinical picture.
Sometimes they occur without gynecological problems, with extragenital diseases, for example, with a violation of the blood coagulation system.
Iatrogenic bleeding
Literally – arising due to the intervention of doctors. Often correlated with taking hormonal drugs, contraceptives, drug treatment, affecting coagulation factors and psycho-emotional state.
This also includes bleeding after insertion of an intrauterine device.
Postpartum hemorrhage

In the period after childbirth, bleeding is caused by a decrease in the tone of the uterus and its contractile abilities, an incompletely born placenta, and disorders of the blood coagulation system.
Normally, after childbirth, lochia is released - physiological hemorrhages, for up to 6-8 weeks. These are long-term, physiological discharges that tend to decrease. Immediately after birth, lochia is more abundant, but after 5–7 days the discharge decreases in volume, which is facilitated by breastfeeding.
Let us note the signs the appearance of which after childbirth should alert a woman:
- Lochia is bright red, lasts for more than 3 days.
- Bloody discharge increases, but should decrease.
- They have an unpleasant, putrid odor.
- Deterioration of general condition (weakness, chills, fever).
This is how infection can manifest itself in the early postpartum period.
Sometimes bleeding appears a month after birth or later. This is an alarming symptom, and the young mother should definitely visit a doctor.
The cause of such discharge may be endometritis, inflammation of the inner lining of the uterine body.
In addition to bloody discharge, a change in the general condition of the body will be observed. Fever, weakness.
When breastfeeding, menstruation may not occur throughout the entire lactation period, so any discharge from the vagina is a signal to be examined. With artificial feeding, the menstrual cycle can be restored within a few months.
Menopause

At this time, uterine bleeding is caused by hormonal imbalances or gynecological diseases. The most common are fibroids, endometriosis, endometrial polyps, and malignant neoplasms.
The climacteric period is divided into several phases:
- Perimenopause is characterized by dysfunctional bleeding caused by hormonal imbalances and menstrual irregularities, physiological for this period. Pathological – caused by diseases, iatrogenic factors.
- Menopause - bleeding predominates due to diseases (fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, etc.), hormonal imbalances, pathology of the endocrine system, problems with blood clotting.
- Postmenopause – the hormonal factor is present only when taking medications containing hormones. All other reasons are caused by diseases.
It must be remembered that in the first two periods a woman is still capable of fertilization. Therefore, bleeding can be caused by spontaneous abortion and complications of such a late pregnancy.
It is especially important to pay attention to cases when bleeding occurs during the period of established menopause. Most often, these are symptoms of a serious illness.
All women know that menstruation is a natural phenomenon that should not be feared or feared. But what to do if the lady is not sure that she has started exactly “ women's days"? What if this is bleeding? This is exactly what this article is about. we'll talk: how to distinguish bleeding from menstruation.
Basic terms
First of all, you need to understand the concepts that will be used in the article. What is menstruation? This is monthly bleeding that is the most important part of every woman's menstrual cycle. At this time, the exfoliated epithelium comes out along with the blood, which lines the uterus in anticipation of conception. In turn, bleeding is the most dangerous phenomenon that indicates pathologies in the female reproductive system (we are talking about uterine bleeding).
Causes of bleeding
Before considering how to distinguish bleeding from menstruation, you need to say a few words about what may cause uterine blood loss.
- Abortions and terminated pregnancies.
- Inflammatory processes of the female genital organs.
- Tumors and neoplasms in the uterus and ovaries.
- Abscesses.
- Infections and intoxications.
Symptoms and signs
So, how can you tell the difference between bleeding and your period? To do this, you need to thoroughly understand what exactly is happening to the female body. A lady is bleeding and not menstruating if:
- The volume of blood released is quite large (exceeds the norm of 80 ml). At the same time, a woman changes her pad more than 8-10 times a day.
- The bleeding does not stop for a week.
- There are disruptions in the menstrual cycle (its duration is less than 21 and more than 35 days).
- Bloody discharge began after menopause.
- There was blood after sexual intercourse.
If at least one of the points is observed in a woman, it is imperative to seek medical advice. After all, bleeding can be an alarm bell and mean that not everything is in order with the body.
Other indicators
How to determine whether a woman is menstruating or bleeding? You need to follow your feelings. What happens to a woman during menstruation is clear. What can happen to a girl’s body during bleeding?
- You may feel weak throughout the body.
- You may feel tired even from the simplest activities.
- The complexion may become pale.
If a woman has bleeding during menstruation, then the following features may also be observed:
- Nails become brittle and pale.
- Hair begins to fall out excessively.
- Menstruation becomes irregular.
- There may be bleeding between periods.
Bleeding and menstruation
Understanding how to distinguish bleeding from menstruation, it is also worth saying that in medical practice there is also the concept of bleeding during menstruation. So, they distinguish:
- Menorrhagia. Very heavy and rather prolonged menstruation.
- Metrorrhagia. This is irregular bleeding that can appear between periods.
- Menometrorrhagia. This is an irregular, but rather long-lasting bleeding.
- Polymenorrhea. In this case, menstruation begins earlier than 21 days have passed since the end of the previous discharge.
Implantation bleeding
It is also necessary to talk about what implantation bleeding is and how to distinguish it from menstruation. First of all, we need to understand the concept itself. In this case, spotting may appear due to the introduction of a fertilized egg into the thickness of the prepared and lined endometrium in the uterine cavity. In this case, minor damage to the blood vessels is possible, which will cause slight blood loss. What can you say about the timing? So, this process occurs in a woman’s body presumably 5-7 days before the onset of menstruation and is often perceived by women as a sign of the onset of menstruation.
What exactly is the difference?
How can you tell the difference between menstruation and implantation bleeding? What do you need to know?
- Duration of bleeding. Implantation does not last long, from several hours to a day.
- Intensity. It is worth saying that implantation discharge is just called bleeding. In fact, very little blood loss occurs, which is significantly inferior to menstrual flow. To maintain hygiene, you only need a panty liner.
- Color. How to distinguish between menstruation and bleeding that occurs during implantation? Just look at their color. Such discharge has a pinkish or yellowish tint, and only streaks of blood can be observed.
- Feel. During the implantation of the egg, a woman may feel a slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen or so-called “bloating.”
- Temperature. If a woman monitors her basal temperature, she should know that during egg implantation the temperature will drop below 37 degrees and then rise sharply.
What can be concluded? How to understand: a woman’s period or bleeding that occurs during the attachment of a fertilized egg to the endometrium? Everything here is extremely simple. During implantation bleeding, a woman loses very little blood, and the discharge most often lasts a couple of hours and is not accompanied by pain.
Postpartum discharge
It is also important to tell women how to distinguish menstruation from bleeding that may occur during the postpartum period. First of all, it must be said that menstruation cannot occur within 60 days after childbirth. Ladies should also remember that, regardless of how the birth took place - naturally or through C-section, the young mother will have some discharge called lochia. In the first ten days they will come with blood, then they will acquire an ichor color and at the very end they will turn yellowish-white. However, in this case, every woman should know that lochia needs to be able to distinguish from bleeding. When should you start sounding the alarm and seeking medical help?
- If lochia has scarlet color even on the 5th day of the child’s birth.
- If there are additional symptoms such as chills, fever.
- If the sanitary pad of a mother who has just given birth is soaked in an hour.
- If a lot of clots come out with the discharge.
- If, after the end of the lochia, the lady begins to have scarlet-colored bloody discharge again.
- If postpartum discharge has an unpleasant odor.
In any case, if a woman is worried about something during the postpartum period, she should definitely consult a doctor for advice. This is the only way to maintain health.
What to do?
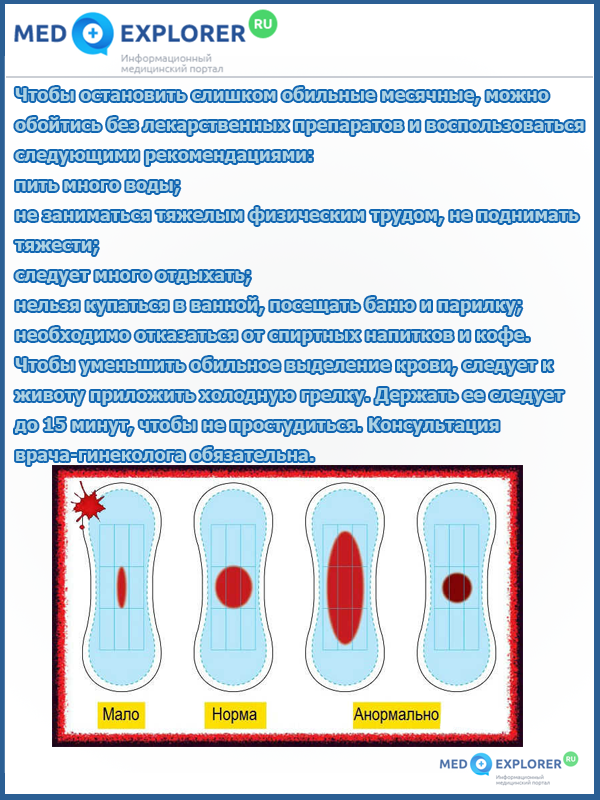
Having figured out how bleeding differs from menstruation, it is also worth saying a few words about how you can stop too heavy menstruation. What can be done for this without using medications?
- You need to drink a lot of water (still).
- During heavy periods, you need to rest more.
- Sports and physical activity are not recommended.
- At this time, it is better for a woman not to lift heavy objects.
- Also, you should not visit a bathhouse, including a steam room, during menstruation.
- You should stop drinking alcoholic beverages and coffee.
To reduce bleeding, apply a cool heating pad to your abdomen. However, you should keep it for no more than 15 minutes, otherwise you may catch a cold.
Medications
Having considered how to recognize bleeding (it differs from menstruation in that the portions of blood are the same), it is also necessary to talk about the fact that you can get rid of this problem with various drugs. What is recommended to use in this case?
- The drug "Ditsinon". It is most often prescribed 5 days before the start of menstruation, in order not to stop, but to prevent bleeding.
- The drug "Vikasol". Most often it is administered intramuscularly along with the drug Oxytocin.
- Medicine "Tranexam". The latest generation drug. However, it must be used carefully, since in certain diseases it can cause the formation of blood clots.
It is also good to take certain vitamins:
- Ascorbic acid.
- Preparations that contain iron (after all, when blood loss occurs, its deficiency occurs).
- Vitamins of groups A and B.
Folk hemostatic agents
We have fully examined how to distinguish bleeding (it differs from menstruation characteristic features, which are described above). Now it’s worth saying a few words about the fact that you can try to stop bleeding and excessive menstruation with the help of folk remedies.
- Nettle. To stop bleeding, you need to drink half a glass of nettle infusion five times a day. To prepare it, you need to pour a tablespoon of the herb with a glass of boiling water, boil everything for 10 minutes and let it brew. It must be said that this infusion will not only reduce blood loss, but also perfectly regulate the menstrual cycle.
- You can also take nettle juice. However, not in its pure form. It must be diluted with water (one teaspoon per 50 ml of water). This medicine is taken 20 minutes before meals.
However, it is worth saying that nettle increases blood clotting. Therefore, not everyone can safely use it.
Orange
Having considered all the options for how to determine whether a woman is menstruating or bleeding, it is also worth saying a few words about how you can still stop uterine bleeding without medication. You can use an orange for this. How to prepare medicine from this citrus? You need to take the peel of 5-6 oranges, pour one and a half liters of boiling water over it and cook until half a liter of water remains. You can add sugar to the broth if desired. You should take it three times a day, 4 teaspoons.
Water pepper herb
To prepare a hemostatic medicine, you need to take one tablespoon of this herb, pour one glass of boiling water and let it all brew thoroughly. Take the medicine one tablespoon three times a day. This remedy can be used for discharge after childbirth, during heavy menstruation, as well as for uterine bleeding.
Kalina
Well, another excellent plant from which you can prepare a hemostatic agent is viburnum.
Recipe 1. You need to take the juice squeezed from these berries, mix it with sugar (one liter will require two kg of sugar). Take the medicine three tablespoons three times a day with water.
Recipe 2. Four tablespoons of dried viburnum berries should be poured with half a liter of boiling water. Place all this in a thermos and leave. The daily dose of medicine will be ready. It should be divided into three equal parts and taken before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Recipe 3. You can prepare an alcoholic extract of viburnum bark. To do this, it must be collected in early spring and dried according to all rules in the open air (not in the sun). It can be used for uterine bleeding, threatened miscarriage, or irregular menstrual cycle.
Recipe 4. It is also good to take liquid extract of viburnum berries when bleeding. The dosage should be no more than 25-30 drops per day.
For each woman, the process of menstrual bleeding is completely individual, depending on the characteristics of the female body. The average duration of the menstrual period is determined to be up to five days. At the same time, if there are any atypical discharges, then it is worth thinking about pathology. However, bleeding should not be ruled out, which can easily be confused with menstruation. Therefore, to provide timely assistance, it is necessary to have an understanding of the distinctive features.
During menstruation, a woman begins to secrete blood in average quantities per day (about 50 ml.). The first days of menstruation are characterized by bloody discharge bright color, then in the following days the discharge becomes darker and is released in portions. The shades of the blood that comes out also differ for each woman individually. Subsequent discharge may occur during sudden rise or movement or physical activity.
Additionally, mucus or blood clots appear in menstrual flow. At the same time, the smell of discharge is also present. Menstrual blood is characterized by an odor reminiscent of fresh meat.

Attention! If the discharge during menstruation has an atypical brown color or the discharge is scanty, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist for advice.
Uterine bleeding and menstruation: main differences
In order to identify pathology, you should interview the patient, who can easily characterize the typical menstrual flow that is characteristic of her. Therefore, any changes should alert the woman. The nature of menstruation can change dramatically, therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the following warning signs:
- The volume of menstrual flow increases significantly.
- The release of blood does not occur in batches, but occurs almost continuously.
- The outgoing discharge is characterized by a too liquid consistency.
- There are no blood clots.
- The color of the discharge becomes deep red.
- There is no specific odor characteristic of blood.
- Signs of anemia are observed.
- There is severe weakness.
- Possible pain in the lower abdomen.
- Before the onset of menstruation, sexual intercourse may cause pain.

Carefully! If the above symptoms are observed, then you should not hesitate to visit a specialist.
Causes of bleeding
For the body, blood loss is enough dangerous manifestation. Almost a third of all uterine bleeding is explained by a pathological process that arose in the female reproductive system. Basically, pathologies of this kind do not pose a threat to life, but lead to poor health, anemia, low levels of iron in the blood, as well as problems with sexual life. Therefore, in order to prevent the occurrence of pathology, you need to know the main reasons that provoke it.

The root causes of bleeding are as follows:
- termination of pregnancy, occurring artificially (abortion) or naturally (miscarriage);
- if delivery occurred by caesarean section;
- frequent diets, which lead to complete intoxication of the entire female body;
- problems with general hormonal levels, sudden disruptions;
- iron deficiency or vitamin deficiency;
- blood diseases;
- blood clotting disorder;
- long-term depressive states, stressful situations;
- illnesses of an infectious nature;
- excessive physical exercise and lifting heavy weights;
- inflammatory process in the reproductive system;
- gynecological pathologies;
- pathological neoplasms.
![]()
Classification of discharge
Experts classify uterine bleeding into three types.
| Bleeding | Short description |
|---|---|
| Normal | Every cycle a woman experiences menstrual flow, which is considered to be a natural norm for the body. |
| Conditionally normal | Discharge occurs in the preovulatory or postovulatory period. Implantation bleeding is also included in the conditionally normal type of bleeding |
| Pathological | These bleedings can occur at any age - during menopause, during the period of reproductive activity, adolescence. They can be divided into subspecies: Functional. Bleeding occurs due to problems with the endocrine system or disruption of the pituitary gland; |

More details about the types of bleeding
Dysfunctional
The main signs of this type of bleeding are heavy blood loss or prolonged bleeding. Adolescent girls and menopausal women are at risk. The provoking factor of the pathology is an excessive amount of estrogen or progesterone. To eliminate this pathology, hormonal therapy is used.
There are two types of dysfunctional blood loss:
- ovulatory. They are characterized by manifestations of an abnormal cycle, that is, over the course of a month, a woman experiences slight discharge of a scanty nature or, conversely, short menstruation that have an interval of more than one month;
- anovulatory. They are characterized by significant blood loss, cycle disruption, poor health, loss of appetite and a constant desire to sleep.
![]()
It is important! Primary pathology can be determined using a gynecological examination, supplemented by ultrasound.
Juvenile
May appear seasonally. This is explained by the fact that the corpus luteum does not form due to hormonal imbalance. If a teenage girl is diagnosed with neoplasms in the reproductive system, then juvenile bleeding cannot be ruled out.

Breakthrough
A third of cases of breakthrough bleeding occur due to problems with the uterus, which are provoked by the intrauterine device. Bleeding can also be caused by the consequences of taking hormonal contraception. To prevent subsequent bleeding, it is recommended to remove the IUD and select the correct dosage of contraceptives.
Profuse
Profuse blood loss is difficult to distinguish from menstrual discharge, since they are also characterized menstrual cramps. The only symptom is increased blood loss, which is characterized by scarlet discharge. The exact period of occurrence is difficult to determine because it varies.
Is it dangerous! Profuse bleeding is difficult to diagnose and requires urgent hospitalization of the woman. In this case it is necessary surgical treatment in the form of curettage of the uterus.
Video - How to distinguish menstruation from bleeding?
Bleeding and menopause
During menopause, a woman cannot exclude the risk of developing neoplasms of various types (fibroids, polyps). This is explained by a decrease in the level of estrogen, which is responsible for the normal menstrual cycle. It is distinctive that a woman will experience severe pain during sexual intercourse, as well as an interval between menstrual cycles of more than three months.
Blood loss during pregnancy
If a woman experiences any bleeding after conception, this is a direct threat to her life and to the fetus. If you notice a woman’s bright bloody discharge, you should immediately call an ambulance. The discharge is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The occurrence of severe pain in the lower abdomen, which resembles contractions.
- Nausea leading to vomiting.
- Increased level of sweating.
- The appearance of dizziness.
Note! The occurrence of bleeding during pregnancy is considered a dangerous sign that threatens life.
How to help
First of all, it is necessary to minimize all physical activity. Then review your diet and include beef, offal (liver), and foods high in iron.
If a woman begins to experience heavy blood loss, she urgently needs to lie down in a position so that the pelvis is slightly elevated. To do this, you can place a pillow or slightly raise your lower limbs. In this way, loss of consciousness can be avoided and symptoms can be reduced.
To reduce bleeding, you will need to apply a cold compress so that the vessels of the uterus constrict and the muscle layer of the uterus contracts.
You should not ignore any pathological discharge, because it can be a sign of a serious illness. A specialist will tell you about the causes of uterine bleeding in a video commentary.
Video - Why do uterine bleeding occur?
Menstrual bleeding is completely individual for all women. On average, it lasts up to five days, begins after an equal number of days, and the amount of blood is also approximately the same. Any changes in the nature of the discharge may indicate the presence of pathology in the body. Heavy periods or bleeding: how to tell the difference?
During “critical days,” an average of about fifty milliliters of blood is released per 24 hours. In the first days they are bright, then they appear darker and appear in portions. Shades of color are also individual. They are repeated with every menstruation. Often portions of blood flow out during physical exertion, sudden standing up, or jumping.
These secretions may contain impurities that are insignificant in quantity and volume - lumps of mucus, clots. The number of lumps is approximately the same for one woman. has a certain peculiar, mild odor, characteristic of the smell of fresh meat.
Difference between menstrual and uterine bleeding
Uterine bleeding from menstruation can be distinguished already at the stage of interviewing the patient. A woman becomes accustomed to the characteristics of her menstrual flow. If they change dramatically, the lady immediately pays attention to it. You should be wary of a situation when the nature of menstruation suddenly changes:
- its volume increases;
- blood flows continuously;
- the discharge acquires a liquid consistency;
- their color changes to scarlet, deep red, crimson;
- clots disappear;
- the specific smell of blood disappears.
Bleeding often occurs earlier than the expected menstruation and lasts more than the usual number of days. Without timely treatment, it can last a week or a month.
Why is this happening
- malignant neoplasms of the uterus;
- benign tumors;
- ovarian diseases with hormonal imbalance;
- adolescence;
- menopause;
- hormonal drugs;
- long-term inflammatory diseases;
- endometriosis;
- pregnancy;
- childbirth;
- blood diseases that cause increased bleeding;
- taking blood thinners.
During adolescence and menopause, the menstrual cycle is often disrupted. If this situation lasts for a long time, the woman gets used to the irregular cycle. Often patients do not immediately notice the appearance of uterine bleeding. Girls who have just begun their first menstruation do not yet know their characteristics and are not able to distinguish the norm from the disease. As a rule, the cycle in adolescents normalizes over time, and the amount of discharge returns to normal.
Taking hormonal contraceptive pills in the first months provokes bleeding. In this situation, you must immediately contact your doctor to determine the advisability of taking these medications. After changing the pills, after several months, the balance of the ratio of sex hormones is restored and such discharge stops.

Benign tumors make themselves felt in two types of bleeding - massive, with discharge large quantity liquid blood without clots or any inclusions, or long-term, with the daily leakage of a small amount of dark blood.
During pregnancy, spotting may occur. The reason here is a rupture of the tube during the development of pregnancy outside the uterine cavity, placental abruption or its incorrect location (at the uterine os itself or directly above it). This situation threatens the development of shock and death of the mother and child.
After childbirth, metrorrhagia is possible due to a complicated birth process (trauma of the birth canal), the development of inflammation of the uterine mucosa, and the remains of a child’s place in the cavity of the reproductive organ.
Symptoms
This condition is dangerous due to the development of hemorrhagic shock or anemia. How to distinguish uterine bleeding from menstrual bleeding? Symptoms that will help you recognize normal periods and bleeding:
- change in the nature of menstruation;
- increasing its duration;
- the volume of blood released increases;
- disappearance of clots.
With significant blood leakage, the amount of fluid in the bloodstream decreases. The patient develops symptoms of shock:
- pads get wet more intensely than usual;
- the woman breaks into a sweat;
- blood pressure decreases;
- the heart beats quickly;
- dizziness occurs;
- chills appear;
- the skin and mucous membranes become pale;
- the body becomes covered with sweat;
- when standing up suddenly, the patient’s condition worsens;
- possible loss of consciousness;
- vomiting may occur;
- facial features become sharper.
When there is a small amount of discharge long time, a woman’s body gets used to it. In this case, anemia develops:
- the discharge becomes lighter than usual over time;
- the woman gets tired quickly;
- there is a feeling of lethargy, drowsiness;
- the skin loses its shine, becomes dry, pale or yellowish;
- nails peel and break quickly, hair falls out;
- often feel dizzy;
- if a woman stands up suddenly, she may lose consciousness;
- rapid heartbeat;
- schoolgirls begin to learn the material poorly;
- In a blood test, the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases.
These symptoms should alert a woman to the need to go and consult a doctor.
Help
Any physical activity should be kept to a minimum. The diet of these patients should include fresh foods, beef, and liver. Dishes are prepared using culinary technologies, steamed.

From the first minutes after the start of intense bleeding, the woman should go to lie down. You need to place a pillow under her pelvis or raise her legs up. This position will prevent the patient from losing consciousness. Symptoms in this condition decrease and blood flow to the head improves.
On the lower abdomen you need to put the most ordinary heating pad with cold water. When exposed to cold, the muscle layer of the uterus contracts, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows, and this helps reduce bleeding.
The patient needs to unfasten tight clothing and remove the belt. You need to open the window slightly to let in fresh air. The patient should drink plenty of fluids in small sips. After this, you need to immediately call an ambulance.
Herbs
Herbalists recommend using decoctions of oak bark, nettle, cinquefoil, wheatgrass, and viburnum bark as effective hemostatic agents. Particularly noteworthy are nettles, rose hips and oak bark. Nettle is rich in vitamin K, rosehip is rich in vitamin C and iron. These compounds can stop bleeding and help prevent anemia.
The bark of oak and viburnum is harvested from older plants. A decoction of them is infused for up to an hour and taken a tablespoon before meals. This way, menstruation will become less heavy, and bleeding will soon stop.
Conclusion
The appearance of intense and prolonged bleeding can lead to the development of anemia or be complicated by shock. A gynecologist knows how to distinguish menstruation. The regimen for such patients should be gentle. As first aid, you need to lay the woman down, place cold on her stomach, and give her something to drink.
We recommend similar articles

























