Symptoms of ovarian pain. Why do the ovaries hurt in women: possible causes.
Pain in the ovaries is not a gynecological disease, but is only a common symptom of many pathologies of the reproductive system. Pain in the ovaries accompany most of the most common gynecological diseases in women and girls of different ages. The pathological process dramatically affects only the ovaries; quite often the uterine appendages are also affected; sometimes the pain becomes persistent; in such cases, such a pathology is called chronic pelvic pain.
Why do the ovaries hurt: the most common causes
Most women believe that pain in the ovaries refers to signs of an inflammatory process, but this is not true. Ovaries hurt during ectopic pregnancy, with the appearance of a cyst, hemorrhage (apoplexy), with torsion of the ovarian pedicle. Below are the most common reasons that cause pain in the areas of projection of the ovaries (iliac regions).
- Inflammation of the ovaries(adnexitis) - the cause of an inflammatory process that can affect not only the ovaries, but also other internal genital organs, are mycoplasmas, candida, chlamydia and ureaplasma; with chlamydia, the infection has no characteristic clinical picture. The main symptom of adnexitis is pain in the lower abdomen and ovaries, the nature of the pain is periodic, painful sensations can also radiate to the lower back. Advanced adnexitis can lead to infertility.Oophoritis is inflammation of the ovarian appendages. Most characteristic symptom - lower abdominal pain, often it radiates to the lumbosacral part of the spine. Wherein it hurts like my right ovary, and left, the pain is usually periodic, less often - constant. The causes of oophoritis are fatigue (mental and physical), hypothermia, decreased immunity caused by other diseases. With oophoritis, when left (or right) ovary hurts, disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system: decreased ability to work, insomnia, weakness and increased irritability.
- Hemorrhage into the ovary(apoplexy) - accompanied by pain, ovarian rupture and bleeding. The first manifestation of bleeding is shooting pain in right ovary(apoplexy of the left is less common), sometimes covering the entire pelvic region. The pain can be so severe that a woman can lose consciousness (if heavy bleeding), the temperature does not rise, the pulse quickens, the pressure drops sharply, cold sweat appears, and vomiting may begin.
A cyst or tumor formation - the pain in this case is constant, due to the pressure that the formation constantly exerts on the pelvic organs and their nerve endings. A twisted tumor or cyst causes circulatory problems, pain, and provokes the onset of an inflammatory process and tissue death. If the size of the cystic capsule is small and it does not undergo changes, this pathology is asymptomatic.
Torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, with violation of the integrity of the formation. Fluid from the cyst enters the abdominal cavity, leading to tissue irritation, ovaries start to hurt. Torsion of the leg, leading to rupture of the cyst or necrosis of its tissue, can cause peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). This situation requires prompt surgical intervention. Peritonitis can begin in the presence of a malignant or benign ovarian tumor.
Ovarian torsion - occurs with increased physical activity and is provoked by high mobility of the ovaries in the pelvis. Torsion occurs most often in girls younger age, especially restless ones. In adult women, torsion can be caused by drug stimulation of ovulation or pregnancy. Signs of torsion are acute pain in the ovaries, vomiting, swelling on palpation.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome - develops during hormonal treatment of female infertility. At the same time, the size of the ovaries increases, numerous follicular cysts appear, and stromal edema is observed. For mild syndrome there is pain in the ovaries, there is an increase in body weight, the stomach swells. The severe form is characterized by hypovolemia (decreased circulating blood volume), accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites), shortness of breath, oliguria (decreased amount of urine produced by the kidneys), and electrolyte imbalance.
Psychogenic factors - diagnosed if the doctor was unable to detect organic causes causing pain in the ovaries. In this case pain in the ovary may be triggered by hysteria or a prolonged depressive state.
Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy: causes
The reasons why pain in the ovaries during pregnancy, similar to those described above. Many of the above pathologies can cause infertility, but if, despite the existing disease, conception has taken place, ovarian disease can lead to serious negative consequences:
- I will have a miscarriage;Defect in fetal development.
Therefore if a woman has pain in the ovary on the right, or on the left, and at the same time, conception is in the immediate plans, it is imperative to find out the cause of the pain and eliminate it.
If ovary pain during pregnancy, and such pain manifests itself after fertilization of the egg, the cause of the pain may not be the ovary at all. The fact is that during pregnancy the uterus and ovaries rise significantly above their standard position. Therefore, in such a case, most likely, it is not the ovary that hurts, but the ligaments that support the ovary and uterus, or the uterine muscles. However, only a specialist can determine for sure whether this is so. Behind pain in the ovaries Intestinal pain can also be taken into account; to make sure of this, you should monitor how regular the pregnant woman’s stool is.
Pain in the ovaries before menstruation and after ovulation
Pain in the ovaries may also be associated with cyclic changes that occur during the menstrual cycle; they are also called ovulatory syndrome. Painful sensations are caused by rupture of the follicle that accompanies the release of the egg. A certain amount of blood pouring out in this case irritates the peritoneum, rich in nerve receptors, for this reason ovary hurts after ovulation.
If ovary hurts before menstruation- this is due to a decrease in estrogen levels (the corpus luteum is not yet formed and is not able to produce progesterone). Because of this, a slight detachment of the endometrium occurs, which is accompanied by pain and spotting for one or two days. With ovulatory syndrome ovary hurts sometimes on the left, sometimes on the right - this is due to the fact that it matures alternately, sometimes in the left and sometimes in the right ovary. Ovulatory syndrome is not a cause for concern, but only indicates the proper functioning of the ovaries.
Pain in the ovaries is disturbing lots of women. In order to determine whether they are a cause for concern, it is better to seek help from a highly qualified specialist. The doctors of our clinic will provide you with qualified assistance, based on your medical history and laboratory tests, they will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment that will help you get rid of pain in the ovaries and avoid possible complications.
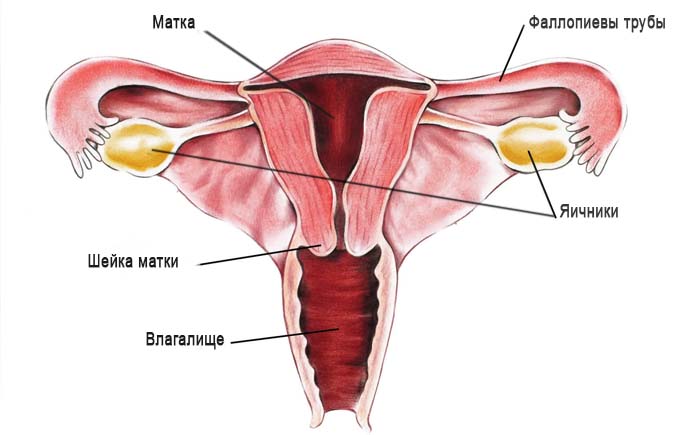
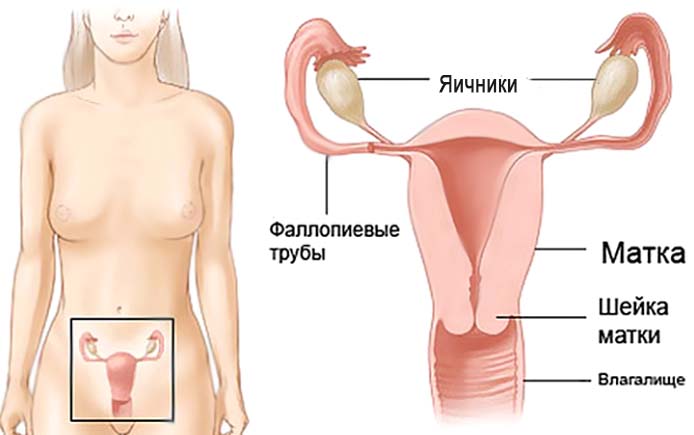
The ovary is a paired female reproductive gland, the site of formation of egg maturation and the production of hormones that regulate the sex life of women. The anatomical structure, reactions to hormonal stimulation and secretory activity of the ovaries are not the same at different periods of life. This chapter examines normal ovarian physiology as a basis for understanding the pathology of both the ovaries themselves and other organs of the female reproductive system.
What diseases cause pain in the right ovary
Causes of pain in the right ovary:- Pain in the right ovary may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the right appendage of the ovary (oophoritis). It is the most characteristic feature of this disease, is localized in the lower abdomen on the right and often extends to the lumbosacral spine. As a rule, pain in the right ovary occurs in attacks, but can also be present constantly. The occurrence of pain and its intensification is facilitated by hypothermia, physical and mental fatigue, decreased immunity against the background of other internal diseases. Such pain is often accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system - increased irritability, weakness, sleep problems, and decreased ability to work.
Adnexitis of the right ovary, or inflammation of the ovary. The most common causative agents of inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs, which lead to inflammation of the ovaries (adnexitis), are chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, and candida. The clinic of chlamydial infection has no characteristic manifestations. Without adequate therapy, the inflammatory process during inflammation of the ovaries (adnexitis) takes a protracted course and leads to infertility. The main sign of inflammation of the right ovary (adnexitis) is pain in the right ovary and lower abdomen on the right. The pain may radiate to the lower back and is almost always dominated by periodic pain.
In some cases, pain in the right ovary occurs when a cyst forms in it. Until the cystic capsule is small in size and does not undergo negative changes, this pathology is asymptomatic.
The cause of constant pain in the right ovary is an ovarian cyst or tumor that has reached a large size. She squeezes the neighboring ones internal organs and nerve endings. Not only neoplasms can become twisted, but also the ovaries themselves. This leads to impaired blood supply and tissue necrosis, inflammation and pain develop.
Pain in the right ovary occurs when the cyst stalk is torsioned or as a result of a violation of its integrity, which is accompanied by the outpouring of liquid contents into the abdominal cavity and causes tissue irritation. In addition to nausea, vomiting and pain, rupture of an ovarian cyst or necrosis of its tissue due to torsion of the leg can provoke inflammation of the peritoneum - peritonitis, which requires immediate surgical intervention. A similar situation can occur in the presence of a benign or malignant ovarian tumor.
Pathological changes in the position of the ovarian appendages are facilitated by their relative mobility in the pelvic cavity, as well as increased physical activity. That is why this pathology is observed, as a rule, in childhood. Among the factors contributing to torsion of the right ovary, it should be noted drug stimulation of ovulation, pregnancy, as well as any conditions accompanied by an increase in the size of the ovaries. Sharp pain in the right ovary and abdomen may be accompanied by vomiting; palpation reveals a painful swelling. If the tissue of the appendages has undergone irreversible pathological changes, surgical removal of the ovary is performed.
Sometimes during ovulation the right ovary ruptures, causing bleeding. The entry of blood into the abdominal cavity provokes pain and threatens the development of peritonitis, therefore surgical intervention is indicated, during which sutures are placed and the integrity of the organ is restored. For some women, ovulation itself is quite painful, as indicated by the appearance of pain in the right ovary on certain days of the menstrual cycle. In addition, acute and chronic inflammatory processes contribute to the formation of adhesions in the right ovary, which in turn often cause pain in the right ovary.
Apoplexy of the right ovary is a sudden hemorrhage into the ovary, which is accompanied by its rupture and bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
Ovarian apoplexy occurs, as a rule, in women under the age of 40, more often in the right ovary, and bleeding and pain always occur in the right ovary. Based on the predominance of one of these signs, anemic and painful forms of the disease are conventionally distinguished. If these signs are equally expressed, they speak of a mixed form of apoplexy.
The disease begins acutely with sudden, sometimes very severe pain in the right ovary and lower abdomen, predominant on the side of the affected ovary. The pain often radiates to the rectum, hip and lower back. Often the attack is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, as well as fainting.
Body temperature remains normal. With heavy bleeding there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure and collapse (a serious condition with severe cardiac weakness, a drop in vascular tone, rapid pulse, and cold sweat). When palpated, the ovary has a spherical shape and sharp pain.
Ovulatory pain in the right ovary occurs in the lower abdomen during the periovulatory period as a result of irritation of the peritoneum by follicular fluid; last from 12 to 36 hours in separate attacks of several hours.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome can develop in women with infertility when treated with hormones (clomiphene, gonadotropins). The ovaries are enlarged, with multiple follicular cysts, a large cystic corpus luteum, and stromal edema. In a mild form, pain appears in the right ovary, bloating; weight gain. In severe cases, shortness of breath, ascites, pleural effusion, electrolyte imbalance, hypovolemia, and oliguria appear.
Psychogenic factors: when excluding organic causes of pain in the right ovary, it is necessary to examine the woman by a psychotherapist ( borderline states: hypochondria, depression, hysteria).
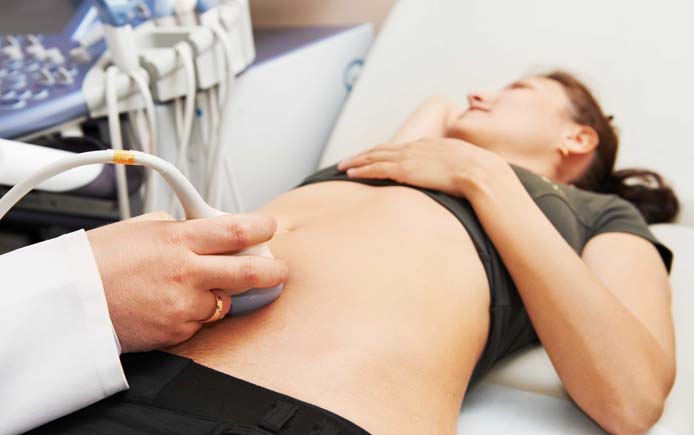
Palpation of the abdomen and gynecological examination help determine the presence of a large ovarian tumor. Important information about the condition of the uterine appendages is provided by pelvic ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostic laparoscopy is especially valuable, allowing to identify adhesions and foci of endometriosis localized in the right ovary. Using this technique, it is possible not only to detect, but also to eliminate many pathologies of the pelvic organs. Competent diagnosis is the key effective treatment, which will allow you to get rid of pain in the right ovary forever.
Which doctors should I contact if there is pain in the right ovary?
Gynecologist
A very common complaint of most women when visiting a gynecologist is pain in the ovaries, the causes of which can be very diverse.
The main causes of this type of pain are:
- diseases of inflammatory etiology;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- the appearance of neoplasms;
- pathological features of the development of the organs of the female reproductive system;
- displacement of the uterus and appendages;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle.
Pain in the ovaries can occur for one of the above reasons or due to a complex of factors, which may be based on serious diseases.
Ovarian diseases
A modern woman lives in a dynamic world, and often “forgets” about the need to regularly visit a gynecologist. Meanwhile, rates of ovarian diseases are increasing every year. The consequences of such a pathology can be quite serious and irreversible, which is why it is so important to notice the first symptoms and consult a specialist.
Dividing ovarian diseases, the following classification is given:
- adnexitis- an inflammatory disease affecting the fallopian tubes and ovaries. The trigger for the disease is infection, including chlamydia, gonococci, and E. coli. Against the background of weakened immunity, adnexitis develops against the background of any infectious disease;
- apoplexy- accompanied by rapid hemorrhage in the ovary and severe sharp pain. Why is this pathology dangerous? Medical assistance is extremely necessary because... blood may enter the abdominal cavity;
- – occur in the ovarian cavity due to the accumulation of secretions. The process of cyst formation is similar to the formation of a tumor; most often, the trigger for the appearance of a formation of this kind is a hormonal imbalance. If several cysts form, polycystic disease is diagnosed;
- cystoma– a benign tumor on the ovary. In most cases, surgical intervention is required to eliminate the risk of transformation into a malignant formation; it may not have associated symptoms;
- tumor- appears from the cells of the ovary itself. Tumors can be benign or malignant. In the latter case we are talking about cancer. Benign tumors without proper control and treatment also tend to develop into oncology.
Ovarian cancer- a real scourge of women. Today, there are several reasons that can provoke cancer of the female reproductive system:
- heredity;
- hormonal disbalance;
- sexually transmitted diseases in advanced form;
- abortions;
- untimely initiation of sexual activity;
- late pregnancy or no pregnancy at all.
Pain in the ovaries can vary in duration and intensity. However, even with minor discomfort, such symptoms should not be overlooked. They can lead to serious and dire consequences, so it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Why does it hurt on the left side?
In most cases, women complain of pain in the lower abdomen on one side. What causes pain in the left or right ovary?
The most common cause is an inflammatory process in one of the ovaries. It is accompanied by attacks of pain, covering not only the lower abdomen, but also the lower back. The main reasons in this case are hypothermia and hormonal imbalance. Even a woman’s behavior changes: she becomes irritable, her performance decreases, and lethargy and apathy appear.
Pain in the left ovary can also be caused by a sexually transmitted infection. On early stages There may be no symptoms, so there is a high probability of the disease becoming chronic. This is where pain begins to appear, which, without proper treatment, tends to intensify over time.
A cyst formed on the left ovary can also cause pain. However, small cysts rarely cause any symptoms. Pain appears when the size of the formation begins to increase, until the capsule ruptures. To avoid serious complications A woman is required to undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs at least once a year.
Pain in the ovarian area may be due to the fact that their location has changed, for example, torsion has occurred. Why is this happening? The ovaries are quite mobile, and therefore susceptible to such pathological changes.
During ovulation, pain in the left ovary, for example, can be natural. However, the temporary nature of the discomfort should also not be ignored and, if the opportunity arises, consult a doctor and find out the objective causes of the pain.
Why does it hurt on the right side?
Most often, the causes of pain on both sides are quite similar. So pain in the right ovary may be a consequence of inflammation or infection. In the most severe cases, it may be a tumor.
In adolescence, girls often complain of pain in the right ovary. This situation is associated with an unstable menstrual cycle and accompanying hormonal dissonance.
Why does pain in the right ovary occur after sexual intercourse? Such manifestations may be due to an unsuccessfully chosen position for sex or insufficient lubrication production.
Pain in the right ovary rarely occurs in women early stages pregnancy when there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy. In this case, urgent medical attention is needed.
Pain and the menstrual cycle
Pain in the right ovary, as well as in the left, may be a sign of the ovulation process. It is from such manifestations that many women know the characteristics of their menstrual cycle.
If the pain is associated with ovulation and is temporary, then the following rules should be followed:
Rule 1. Exclude physical exercise. Stay at rest for as long as possible.
Rule 2. Avoid stress. Do not participate in conflict and controversial situations.
Rule 3. Eat well.
Rule 4. Give up bad habits.
For these types of pain, you can take painkillers, but only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Self-treatment for pain of this kind is contraindicated. It will not only be useless, but can cause significant harm to health.
The ovaries are paired organs of the female reproductive system. They react to any pathological changes in the body, from infection to disruptions in the functioning of the hormonal system. The appearance of pain is a signal of problems at work, and as a rule, these problems are associated with serious illnesses.
In addition, pain in the lower abdomen can act as symptoms of a disease of related organs, for example, appendicitis with sharp pain, or in the pelvis if the pain is aching. Ignoring pain in the lower abdomen is extremely dangerous!
To exclude complications and for prevention purposes, every woman should visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year and undergo a pelvic ultrasound annually, unless there are additional recommendations from a doctor.
Many women face the problem of pain in the ovarian area. Often ladies do not pay attention to this, but there are those who think about it seriously. In this article we will take a closer look at the question: “Why do the ovaries hurt?”
Causes
Girls don't think about their health at all when they wear revealing outfits in cold weather. Nylon tights, jeans on bare legs, sitting in the snow in winter - all this provokes inflammatory processes. Often a girl is not even aware of her illness, continuing to dress lightly. In addition, they can provoke inflammation. This is the main answer to the question of why the ovaries hurt.
Causes and types of inflammation
Even if a girl dresses warmly and has no infections, there is still a risk of inflammation. Poor immunity, poor nutrition, bad habits - all this provokes inflammatory processes.

We already know why - due to inflammation. There are two types - adnexitis and oophoritis. With the ovary itself, and with oophoritis - its appendages. The girl will not be able to independently determine what type of disease it is. The symptoms are very similar to each other: pain, sharp or wave-like, throbbing or constant. Girls often ask why their ovaries hurt on the first day of menstruation. This is a common occurrence for nulliparous young women.
The reasons why pain occurs can be associated not only with inflammatory processes. If a girl experiences pain depending on her position and movement, this often means that a cyst is beginning to form. Then an operation is necessary to remove the formation that is causing the ovaries pain.
Reasons that should be identified in time
Excessive physical activity can cause nerve endings to become compressed. Sometimes such problems arise due to hormone therapy and pathologies. It is extremely important to identify the causes of pain, since delaying treatment can lead to infertility.
Why else could there be pain in the ovaries?
The reasons may not mean that the girl is sick. Pain in the ovarian area sometimes occurs due to ovulation. Some women experience severe pain during this period - this is due to the fact that the ovary has burst at the moment. In this case, bloody discharge also bothers the girl.
Ovarian apoplexy
Sometimes a woman may feel so much pain that she faints. The cause is hemorrhage into the ovarian cavity. In this case, the integrity of the membrane is compromised, and there is a risk of peritonitis. In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as the consequences can be very serious.
 Tumor
Tumor
Often pain occurs due to a tumor in the ovaries. This phenomenon is becoming very common due to poor ecology. There is no need to be scared or despair, since in most cases this disease is curable. In this case, surgery will be performed to remove the tumor. Then the woman needs to undergo a series of procedures.
What if the reason was not found?
If doctors still do not find out why the ovaries hurt, the causes of this illness could not be determined, then additional examination is carried out. Sometimes it happens that the woman’s hysterical character is to blame, that is, the problem is of a psychogenic nature.
The functioning of the female body is aimed primarily at giving birth to children. Ideally, all our organs should work correctly. But, unfortunately, this is not always the case, and we are all susceptible to illness. Women often complain of pain in the lower abdomen, saying that their ovaries hurt. So how do the ovaries really hurt?
First you need to understand what ovaries are. These are female paired organs of the reproductive system, located on both sides of the uterus and producing female hormones estrogens and gestagens. The cause of pain in the ovaries can be various diseases of these organs: adnexitis, oophoritis, cyst or tumor, ectopic pregnancy. You can read more in our other article - “”.
Where do the ovaries hurt? These are pains in the lower abdomen and back, but they can be symptoms of other diseases not related to the ovaries. The question of whether the ovaries may hurt, or whether you have some other disease, can only be decided by a doctor. You should not take various pills yourself, warm up painful areas, or, in general, self-medicate. This can lead to serious consequences.
How to understand what exactly the ovaries hurt? Symptoms may vary.
Symptoms of adnexitis
Adnexitis is an inflammation of the ovaries. These are cutting and stabbing pains that occur at regular intervals in the lower abdomen. The pain may radiate to the back or legs. Sometimes the pain is so intense that the woman cannot even straighten up. The treatment is carried out by a doctor. In principle, with adequate treatment, recovery occurs quite quickly, the main thing is that the disease does not become chronic.
Symptoms of oophoritis
Inflammation of the ovarian appendages. With oophoritis, pain appears in the lower abdomen and sharp pain in the ovaries. They differ from the pain of adnexitis in their paroxysmal nature, sometimes aching pain occurs. These pains are also accompanied by decreased immunity, lethargy and weakness, irritability and sleep disturbances.
Symptoms of ovarian cysts
Cyst is a common gynecological disease. Can a cyst hurt? A cyst, or ovarian tumor, which has greatly increased in size, begins to put pressure on nearby organs, which leads to pain. Sometimes it breaks. All this leads to the development of the inflammatory process. Pain from a cyst is mainly localized in the back and resembles osteochondrosis. To avoid rupture of the cyst and, as a result, peritonitis, if such pain occurs, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms during ovulation
During ovulation, the egg is released from the follicle, and sometimes this process is accompanied by minor bleeding and dull pain in the ovarian area. With adhesions, women also feel pain due to chronic inflammation.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
In this case, women experience cramping pain on the side where the pregnancy occurred, which requires hospitalization and emergency surgery.
Thus, it becomes clear that pain in the lower abdomen and back can appear as a result of various diseases, including ovarian diseases. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, and he will also prescribe treatment. A woman should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication; this can be extremely dangerous and lead not only to the appearance of a chronic form of the disease, but even to death, as, for example, as a result of a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, you should be very attentive to your health and take care of yourself!



















