The person appointed responsible for fire safety is obliged. Fire safety requirements: what a personnel officer should remember
System fire safety in the Republic of Belarus includes a set of economic, social, organizational, scientific, technical and legal measures aimed at preventing and eliminating fires.
Responsibility for fire safety of the enterprise rests with managers enterprises. At each production facility (workshop, laboratory, warehouse, etc.), a person responsible for fire safety is appointed by order. The names of responsible persons must be posted in prominent places.
Responsibilities of managers and officials of the enterprise:
1) ensure fire safety (fire safety) and fire safety regime at the enterprise
2) ensures implementation and compliance with fire safety requirements, norms, standards, rules during the design, reconstruction, repair of subordinate facilities
3) create freelance firefighting units and organize their work
4) organize training for workers on industrial safety rules
5) ensure the development of an action plan for workers in case of a fire
6) take measures against violators of fire safety norms and rules, recover material damage from those responsible for fires
Persons responsible for the safety of premises must:
1) explain labor safety rules to employees and demand strict compliance with them
2) monitor the good condition of the equipment
3) know where fire extinguishing means are located and be able to use them
4) before completing work, check that work areas are thoroughly cleaned, and after completion, check that the voltage is turned off
Responsibilities of employees:
Know and comply with fire safety requirements;
Take precautions when working with flammable and combustible substances;
If a fire is detected, report it to the fire service and take possible measures to save people, property and extinguish the fire.
In production, administrative and warehouse premises, telephone numbers must be posted with signs indicating the telephone number. fire service.
Fire service at the enterprise is carried out by a paramilitary security unit or fire protection units, which in their activities are subordinate to the head of the enterprise.
They are entrusted with:
- development of fire prevention and fire prevention measures
- carrying out explanatory work on compliance with fire safety measures and rules
- extinguishing fires and ignitions on the territory of the enterprise and nearby
Enterprises create volunteer fire brigades
The composition of the voluntary fire brigade is determined by the head of the enterprise at the rate of five people for every hundred employees. If the enterprise employs less than one hundred people, the number of fire brigade members must be at least ten people. There must be members of this squad in every workshop and shift. DPD structure: commander, senior combat crew and members of the DPD.
Engineering and technical workers, workers and employees bear personal responsibility for compliance with fire safety rules, in particular those relating to their profession. activities, which should be reflected in their job responsibilities.
Persons who violate or fail to comply with the Law of the Republic of Belarus “On Fire Safety”, standards, norms and rules of fire safety, as well as persons responsible for causing fires, bear disciplinary, material, administrative and criminal liability in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Belarus.
Disciplinary responsibility consists of imposing penalties in the form of a reprimand, reprimand, severe reprimand and even dismissal (Article 198-204 of the Labor Code).
An employee may be involved in financial liability, if, through his fault, the enterprise suffered material damage (Article 400 of the Labor Code, Regulations on the implementation of State Fire Supervision and Resolution of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of June 25, 2003 No. 26).
Administrative responsibility is manifested by measures of administrative coercion and suppression (Article 170 of the Code of the Republic of Belarus on Administrative Offenses (CAO)).
To measures of administrative coercion include: warning or imposing a fine on officials, workers and citizens for violating fire safety rules or failure to comply with instructions and resolutions.
To measures of administrative restraint include: suspension of enterprise operations, repairs of facilities; prohibition of the operation of buildings, machines, devices and other devices operating in violation of fire safety requirements; a ban on the production, sale and use of products that do not meet fire safety requirements.
In addition to administrative measures, there are also criminal liability, defined in the relevant articles of the Criminal Code of the Republic of Belarus.
Art. 304 CC regulates the following:
1. Violation of fire safety rules by a person responsible for their implementation, resulting in a fire, committed within a year after the imposition of an administrative penalty for violation of fire safety rules,
Punishable fine, or correctional labor for a period of up to one year, or arrest, for a period of up to three months with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities.
2. Violation of fire safety rules by a person responsible for their implementation, which through negligence resulted in a fire causing serious or less serious bodily injury or damage on a large scale,
Punishable by correctional labor for a term of up to two years, or arrest for a term of up to six months, or restriction of freedom for a term of up to three years, or imprisonment for the same term with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities or without deprivation.
3. The act provided for in part two of this article, which entailed negligence death of a person or causing grievous bodily harm to two or more persons,
Punishable imprisonment for up to seven years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities.
4. Deliberate destruction or damage to property committed in a generally dangerous manner, such as arson, or causing damage on a large scale (an amount of two hundred and fifty or more times the base amount established on the day the crime was committed),
Punishable by restriction of freedom for a term of up to five years or imprisonment for a term of three to ten years (Article 218 of the Criminal Code).
In each workshop, laboratory, workshop, specific instructions on fire safety measures must be developed (approved by the chief engineer).
To prevent fires at enterprises, organizational, operational, technical and regime measures.
1. Organizational arrangements - This proper organization of the fire protection of the facility, training workers in fire safety, conducting fire safety briefings and technical minimums, conversations, creating volunteer fire brigades, using visual propaganda, etc.
Each new hire must undergo fire safety training before starting to perform his duties, and in especially fire- and explosion-hazardous enterprises, all employees must undergo a fire safety training minimum.
Fire safety training carried out in two stages - introductory and on-the-job training.
- Introductory fire safety All newly hired workers and employees must undergo training on compliance with fire safety measures. To conduct initial fire safety training at the enterprise, d.b. a room equipped with the necessary visual aids has been allocated. Introductory fire safety training can be carried out simultaneously with safety training. New hires must be familiar with general rules and fire safety instructions. safety, the procedure for conducting hot work, with workshops in high-risk areas, possible reasons fires and communications and fire extinguishing equipment.
- primary- carried out at the workplace by a person responsible for the fire safety of the workshop, production area, etc. carried out by the head of the workshop or, on his behalf, by an employee responsible for the fire safety condition. carried out directly at the production site where the newly hired person will work and are introduced to the fire safety rules. safety in this workshop, with increased fire safety installed. hazards, fire extinguishing means and the benefits of conducting briefings are recorded in a log.
Fire technical minimum are carried out in the form of classes according to a special program developed taking into account the fire hazard characteristics of the technological installation. IN in this case detailed training of workers in the techniques and methods of using available personal protective equipment, fire extinguishing and fire alarm equipment is provided.
Training according to the fire-technical minimum program should be carried out directly in workshops, installations, and production facilities. areas. Classes are conducted in groups, taking into account the category of specialists. Upon completion of the fire-technical minimum program, workers and employees are given credits. The test results are documented in a special statement, in which grades on the topics studied are indicated.
2.Operational measures provide for timely preventive inspections, repairs, tests of technological, auxiliary and engineering equipment, as well as the correct maintenance of buildings and structures.
3. Technical measures- This strict adherence to fire safety rules when designing buildings and structures, equipment layout, heating, lighting, ventilation, etc.
4. Events regime nature represent the prohibition or designation of smoking areas, measures for the safe organization of welding and other hot work, compliance with fire safety regulations, etc.
Under fire protection regime enterprises understand a set of fire safety measures when performing work and operating facilities, i.e. a set of fire safety measures and requirements that are pre-established for an object or individual premises and are subject to mandatory compliance by all persons working there.
The fire safety regime is established by rules, instructions, orders or orders of the head of the facility and covers such preventive measures as maintaining the territory and premises, passages, evacuation routes in buildings, de-energizing electrical equipment at the end of the working day and in case of fire, cleaning premises and workplaces, establishing and compliance with the standards for storing raw materials, semi-finished products and finished products in the premises, prohibiting smoking and the use of open flames in fire hazardous areas, as well as regular inspections before closing the premises after completion of work.
Fire safety is a concept that applies not only to business entities, but also to ordinary citizens. To feel completely safe from natural Disasters such as a fire, all citizens should be aware of their rights and responsibilities in this area.
Rights and responsibilities of citizens in the field of fire safety
The rights of citizens in the field of fire safety include:
Responsibilities in the field of fire safety of citizens include:
Responsibility for non-compliance with fire safety standards and regulations
Owners of property, managers of enterprises and authorized persons responsible for fire safety are responsible for failure to comply with fire safety obligations.
For violation of fire safety requirements in residential buildings, apartments and rooms, responsibility rests with tenants and tenants unless otherwise provided by the contract.
Thus, for violation of the fire safety regime, the requirements of standards, rules and regulations and fire safety regulations, which resulted in a fire that resulted in harm to the life and health of people, officials are subject to penalties in the form of fines and even imprisonment for up to 3 years .
Responsibilities of organizations in the field of fire safety
One of the most significant documents for fire safety at any enterprise is the federal law “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements”, which sets out in detail all the main preventive measures, the algorithm for extinguishing fires and the responsibilities of participants in the labor process. In addition, this document clearly sets out the main criteria for compliance of a business facility with fire safety requirements.
The main task of ensuring fire safety lies with the management of the organization. These responsibilities include:
Fire safety and personal responsibility
In any organization, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the key role in ensuring compliance with fire safety standards is assigned to the head of the enterprise. Thus, by order of management, specialized instructions are issued on the establishment of a fire safety regime at the enterprise. This instruction must contain the following:
Companies specializing in the storage, processing and use of hazardous, flammable and toxic substances are required to warn fire services about the specifics of working materials or finished products in order to avoid unforeseen situations in the event of fires.
The responsibilities of the manager or owner of the enterprise upon arrival at the scene of a fire include:
In addition to the listed measures, the head of the organization must inform fire service workers about all technological and architectural features structures, the number of household premises and potentially hazardous materials and substances stored in them.
Responsibilities of workers to ensure fire safety
In addition to the head of the organization, each of the employees bears responsibility. Depending on the position held, each employee is responsible for organizing fire safety in a separate department.
Chief specialists and heads of production departments are responsible for organizing fire prevention work in individual departments, developing and implementing preventive fire safety measures in the areas entrusted to them.
Enterprise specialists are persons responsible for work to prevent the occurrence and prevention of fires. The list of their responsibilities includes a set of measures to train middle managers and ordinary workers in the basics of fire safety, develop, together with management, instructions on fire safety measures at the enterprise, introduce innovative technologies with minimal fire and explosion hazards, and use advanced installations and fire extinguishing means.
Managers of workshops and other primary departments are responsible for the technical serviceability of structures, mechanisms, ventilation systems and lightning rods, equipping service vehicles with fire extinguishing means, ensuring timely testing of various installations, machines and electrical equipment, as well as not allowing employees to work who have not undergone primary fire safety training and uncertified mechanisms.
1. General Provisions
1.1. This Instruction defines the responsibility of the person responsible for fire safety at facilities, workshops, production areas, administrative buildings, etc. 
1.2. Responsibility for ensuring fire safety of JSC "________" as a whole, in accordance with current legislation Russian Federation, is assigned to General Director.
1.3. Responsibility for fire safety of hazardous industrial facilities, divisions, departments, services, production, office and other premises and territories lies with their superiors, managers, managers, as well as other officials specially appointed by order of the General Director, directors of branches, independent structural divisions.
1.4. The person responsible for fire safety is personally responsible for the implementation of this Instruction in the manner prescribed by law.
2. Responsibility of the person responsible for fire safety
The person responsible for fire safety MUST:
2.1. premises, equipment, as well as materials and substances used and stored in the serviced area;
2.2. Know the current Fire Safety Rules and Instructions for the general fire safety regime, as well as for individual fire-hazardous premises, production operations, and work.
2.3. Monitor the condition of the territories, escape routes and exits are NOT ALLOWED:
2.3.1. blocking the approaches to buildings, fire hydrants located in the area adjacent to the buildings;
2.3.2. obstruction of passages, corridors, vestibules, elevator halls, landings, flights of stairs, hatches with furniture, cabinets, equipment, various materials and objects that impede the free exit of people and the evacuation of property in the event of a fire;
2.3.3. removing devices for self-closing doors, fixing self-closing doors of staircases, corridors, vestibules, halls in the open position.
2.4. Monitor the serviceability of primary fire extinguishing equipment (fire hydrants, fire extinguishers, asbestos blankets) and ensure clear access to them. Know the location of primary fire extinguishing equipment. Know how to use them to extinguish a fire.
2.5. Know the location of fire alarm and communication equipment (telephones, detectors, fire alarm buttons). Know how to use them to call fire departments. Explain to subordinate personnel the fire safety requirements in force at the facility and the procedure for action in the event of a fire.
2.6. Conduct primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted workplace fire safety briefings with workers and employees of your department, service, unit, recording the results in a special journal (Appendix No. 4). Do not allow persons who have not been trained to work.
2.7. Constantly monitor compliance by workers and employees with fire safety measures, the established fire safety regime, as well as the timely implementation of fire safety measures proposed by an authorized official.
2.8. Do not allow temporary fire hazardous work (electric and gas welding, metal cutting, etc.) to be carried out in the premises and on the territory of the facility without a specially issued work permit.
2.9. Every day at the end of the working day, before closing, carefully inspect all serviced premises and check:
2.9.1. turning off electric heating devices, electrical installations, units, machines, equipment, power and electrical lighting networks (with the exception of power supplies and electrical installations, which, according to the conditions of the technological process, must operate around the clock);
2.9.2. cleaning of premises, workplaces industrial waste and garbage;
2.9.3. removal of flammable and combustible liquids and goods in aerosol packaging from workplaces to a specially designated and equipped place for their storage;
2.9.4. the presence of free passages along corridors, stairs to emergency exits, hatches, windows, fire extinguishing and communications equipment;
2.9.5. compliance with fire safety requirements set out in instructions for inspection of premises.
2.10. When inspecting and checking the premises, you should determine whether there is smoke, a burning smell, an increase in temperature and other signs of fire. 
2.11. Inspection of premises where fire hazardous work was carried out must be carried out with special care. These premises must be monitored for three hours after completion of fire hazardous work.
2.12. Premises can be closed only after they have been inspected and all fire hazards have been eliminated. About shortcomings that cannot be eliminated by the inspector, the latter must immediately report to a higher official so that appropriate measures can be taken.
2.13. After closing the premises, windows (windows), the responsible person is obliged to hand over the keys against signature to the security or the responsible person on duty at the facility and make an entry in a special journal about the results of the inspection of the premises.
3. Procedure in case of fire.
3.1. When the warning and evacuation control system is activated, the person responsible for fire safety must act in accordance with the instructions for its operation.
If a fire or signs of combustion are detected (smoke, burning smell, increased temperature, etc.), the person responsible for fire safety MUST:
3.2. immediately call the fire department by calling "01". When calling the fire department, you must provide: the address of the facility, the location of the fire, and your last name. If one of the employees has already reported the fire, then regardless of this, it is necessary to duplicate the message and notify senior management;
3.3. take measures to evacuate people not involved in extinguishing the fire from the danger zone in accordance with the evacuation plan and instructions for operating the warning and evacuation control system (in the event of a threat to people’s lives, immediately organize their rescue using available forces and means);
3.4. simultaneously with the evacuation, guided by the memo on behavior in case of fire, organize its extinguishing with primary fire extinguishing agents in compliance with the requirements of safety measures;
3.5. take, if possible, measures to preserve material assets;
3.6. stop all work, remove all employees not involved in fire extinguishing outside the danger zone;
3.7. check the activation of automatic fire protection systems (fire extinguishing, warning people about a fire, evacuation control, etc.);
3.8. if necessary, turn off the electricity (except for fire protection systems), stop the operation of equipment, devices, shut off gas, steam and other communications, stop the operation of ventilation systems in the burning and adjacent rooms, take other measures to help prevent the development of fire and smoke in the premises building;
3.9. provide general guidance on fire extinguishing until the arrival of the fire brigade;
Organize the protection of the fire site and a meeting of fire departments, inform the first arriving fire chief about the measures taken, and act on his instructions.
Basic concepts of fire safety
Fire safety is the state of protecting individuals, property, society and the state from fires. Ensuring fire safety is one of the most important functions of the state.
Elements of the fire safety system (FSSS) are state authorities, local governments, organizations, peasant (farm) households and other legal entities, regardless of their organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership, citizens taking part in ensuring fire safety in accordance with legislation of the Russian Federation.
Achieving fire safety is facilitated by:
- legal regulation and implementation of government measures in the field of fire safety; 
- creation of fire protection and organization of its activities;
- development and implementation of fire safety measures;
- implementation of rights, duties and responsibilities in the field of fire safety; - production of fire-technical products;
- performance of works and services in the field of fire safety;
- conducting fire prevention propaganda and training the population in fire safety measures; - Information Support in the field of fire safety;
- accounting of fires and their consequences;
- implementation of State Fire Supervision (SFS) and other control functions to ensure fire safety;
- fire extinguishing and emergency rescue operations (ASR);
- establishment of a special fire regime;
This is all! - scientific and technical support of fire safety;
- licensing of activities in the field of fire safety and confirmation of compliance of products and services in the field of fire safety.
Persons responsible for violating fire safety requirements, other citizens for violating fire safety requirements, as well as for other offenses in the field of fire safety may be subject to disciplinary, administrative or criminal liability in accordance with current legislation.
Fire is an uncontrolled combustion that causes material damage, harm to the life and health of citizens, and the interests of society and the state. Fire safety of an object is the state of an object, characterized by the ability to prevent the occurrence and development of a fire, as well as the impact of dangerous fire factors on people and property. The fire safety of the facility must be ensured by fire prevention and fire protection systems, including organizational and technical measures. Fire regime - rules of behavior for people, procedures for maintaining premises and territories, ensuring the prevention of violations of fire safety requirements and extinguishing fires. Fire safety measures - actions to ensure fire safety, including compliance with fire safety requirements.
Regulatory documents in the field of fire safety
The following main regulatory documents are in force on the territory of the Russian Federation:
Federal Law No. 69-FZ “On Fire Safety”;
Fire regulations in the Russian Federation (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 25, 2012 N 390);
Federal Law No. 123-FZ “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements”;
Federal Law No. 384-FZ “Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures”.
General requirements for fire prevention
A fire is impossible under any circumstances if contact of the ignition source with flammable material is excluded (based on this principle, sections of fire safety rules are developed aimed at preventing and extinguishing fires).
If a potential source of ignition and flammable environment cannot be completely eliminated from the technological process, then this equipment or the room in which it is located must be reliably protected by automatic means:
Emergency shutdown of equipment.
Various alarms.
Premises category “A” increased explosion and fire hazard
rooms containing flammable gases, flammable liquids with a flash point of not more than 28ºС in such quantities that they can form vapor-gas mixtures, upon ignition of which a calculated excess explosion pressure in the room develops exceeding 5 kPa, or substances and materials capable of exploding and burning when interacting with water, atmospheric oxygen or with each other in such quantities that the calculated excess explosion pressure in the room exceeds 5 kPa.
Premises category "B" fire and explosion hazardous
rooms in which flammable dusts or fibers, flammable liquids with a flash point of more than 28ºС, flammable liquids are in such quantities that they can form explosive dust-air and steam-air mixtures, upon ignition of which a calculated excess explosion pressure in the room develops in excess of 5 kPa.
Room category "B1" - "B4" fire hazardous
rooms in which flammable and low-flammable liquids, solid flammable and low-flammable substances and materials (including dust and fibers), substances and materials located in the room are capable of burning when interacting with water, air oxygen or with each other, provided that that the premises in which they are available or circulated do not belong to categories A or B.
Room category "G" moderate fire hazard
rooms in which non-combustible substances and materials are located in a hot, incandescent or molten state, the processing of which is accompanied by the release of radiant heat, sparks and flames; flammable gases, liquids and solids that are burned or disposed of as fuel.
Premises category "D" reduced fire hazard
rooms containing non-combustible substances and materials in a cold state. 
Fire hazards
Fire Hazardous Factor (FHF) is a fire factor, the impact of which leads to material damage:
open flames and sparks;
toxic combustion products;
smoke;
consequences of destruction and damage to the object;
hazardous factors resulting from an explosion (shock wave, flame, collapse of structures and scattering of fragments, formation of harmful substances with a concentration in the air significantly higher than the maximum permissible concentration).
Fire hazards affecting people and property include:
flames and sparks;
heat flow;
increased ambient temperature;
increased concentration of toxic combustion and thermal decomposition products;
reduced oxygen concentration;
reduced visibility in smoke.
Associated manifestations of fire hazards include:
fragments, parts of collapsed buildings, structures, structures, Vehicle, technological installations, equipment, units, products and other property;
radioactive and toxic substances and materials that got into environment from destroyed technological installations, equipment, units, products and other property;
removal of high voltage to conductive parts of technological installations, equipment, units, products and other property;
hazardous factors of an explosion resulting from a fire;
exposure to fire extinguishing agents.
Flames most often affect exposed areas of the body. Burns from burning clothing, which are difficult to extinguish and throw off, are very dangerous. Clothes made from synthetic fabrics are especially flammable. The temperature threshold for human tissue viability is 45 °C.
Increased ambient temperature
It leads to disruption of the thermal regime of the human body, causes overheating, deterioration of health due to the intensive removal of salts necessary for the body, disturbances in the rhythm of breathing, activity of the heart and blood vessels. It is necessary to avoid prolonged exposure to infrared rays with an intensity of about 540 W/m.
Toxic combustion products
The composition of combustion products depends on the composition of the burning substance and the conditions under which it burns. During combustion, first of all, a large amount of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides are released, which fill the volume of the room in which the combustion occurs and create concentrations dangerous to human life.
Fire conditions and stages
The fire begins to spread
For a fire to occur, three conditions must be present:
Combustible environment.
Ignition source - open fire, chemical reaction, electric current.
The presence of an oxidizing agent, such as atmospheric oxygen. 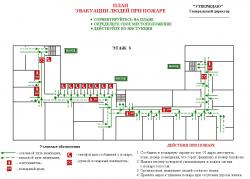
The essence of combustion is as follows: heating the ignition sources of a combustible material before its thermal decomposition begins. The process of thermal decomposition produces carbon monoxide, water and a large number of heat. Also highlighted carbon dioxide and soot that settles on the surrounding terrain. The time from the start of ignition of a flammable material to its ignition is called the ignition time.
The maximum ignition time can be several months.
From the moment of ignition, a fire begins.
Stages of indoor fire
During the first 10-20 minutes, the fire spreads linearly along the combustible material. At this time, the room is filled with smoke; It is impossible to see the flame at this time. The air temperature rises in the room to 250-300 degrees. This is the ignition temperature of the main combustible materials.
After 20 minutes, the volumetric spread of the fire begins.
After another 10 minutes, the glazing begins to fail. The influx of fresh air increases, and the development of the fire progresses sharply. The temperature reaches 900 degrees.
Burnout phase. Within 10 minutes maximum speed fire.
After the main substances burn out, the fire stabilization phase occurs (from 20 minutes to 5 hours). If the fire cannot spread to other rooms, the fire goes outside.
Fire prevention methods
Fire prevention methods are divided into:
reducing the likelihood of a fire (preventive);
protection and rescue of people from fire.
Preventing the spread of fire is achieved by measures that limit the area, intensity and duration of burning. These include:
constructive and space-planning solutions that prevent the spread of fire hazards throughout the room, between rooms, between groups of rooms with different functional fire hazards, between floors and sections, between fire compartments, as well as between buildings;
fire hazard limitation building materials, used in the surface layers of building structures, including roofs, finishing and cladding of facades, premises and escape routes;
reduction of technological explosion and fire hazards of premises and buildings;
availability of primary, including automatic and imported fire extinguishing means; alarm and fire warning.
Preventive actions
Household actions that reduce the likelihood of a fire:
Electrical wiring is insulated to avoid short circuits that could lead to fire.
Insulate sockets located in bathrooms and on external walls from moisture.
Install RCDs and automatic fuses.
Gas and electric stoves are thermally insulated from wooden furniture.
Ashtrays are used to extinguish cigarette butts, and candles are lit in candlesticks.
Also, all employees of Russian enterprises must study the fire safety technical minimum.
Defensive actions
Protection directly from fire is divided into human protection from high temperature and from often more dangerous toxic substances released into the air during a fire. They use thermally insulating clothing BOP (firefighter's combat clothing), insulating gas masks and compressed air apparatus, and air-filtering hoods similar to gas masks.
Fire trucks
Sand box installed for fire protection purposes
Active fire fighting (fire extinguishing) is carried out with fire extinguishers of various fillings, sand and other non-flammable materials that prevent the fire from spreading and burning. Also sometimes the fire is knocked down by a blast wave.
To self-evacuate people from burning buildings, a winch is used, attached to the outside of the window, along which people living on high floors can go down to the ground. Fireproof safes are used to protect valuables and documents from fire.
Job description of a fire safety engineer
I APPROVED
(position of the head of the organization)
________________________________________
(name of company)
________________________________________
(Full name of the head)
< _____ >______________ 200_ g.
Job description
Fire safety engineer
1. General Provisions.
1.1. This job description has been developed in accordance with
legislation of the Russian Federation, Federal Law N 69-FZ "On Fire
safety" and other current regulations of the Russian Federation.
1.2. This job description defines the functional
duties, rights, responsibilities and scope of activity of an engineer
fire safety 
1.3. For the position of fire safety engineer (hereinafter -
Engineer) is appointed a person who has a higher technical education or
secondary technical education and work experience of at least three years.
1.4. An engineer is appointed to a position and dismissed from a position
by order ______________________________________________________________.
(name of the position of the head of the organization)
1.5. The engineer reports directly to __________________________,
(enterprise manager, chief engineer, other)
and in his absence _____________________________, determined by order
head of the enterprise.
1.6. During the absence of the Engineer, his duties are performed by
employee appointed by the head of the organization.
2. Functional responsibilities.
2.1. A fire safety engineer must know:
- orders, rules, instructions, regulations in force at the enterprise
on fire safety issues;
- legislative and regulatory technical documents, methodological
materials on fire safety issues;
- main production processes of the enterprise, features
operation of equipment used at the enterprise;
- measures aimed at preventing fire at the enterprise,
equipment, methods and techniques for ensuring fire safety;
- technical means and methods of their use to ensure
fire safety, fire prevention and extinguishing;
- main causes of fires and explosions;
- organizational basis for ensuring fire safety in
enterprise;
- is obliged to conduct an analysis of the fire safety of the enterprise,
development of orders, instructions and regulations establishing proper
fire safety regime at the enterprise, training of workers in accordance with
enterprise fire safety measures;
- is obliged to organize and control the passage of all technical and technical equipment,
workers and employees of fire safety briefings conducted
responsible for fire safety in departments of the enterprise in
in accordance with the requirements of GOST "Organization of training for workers
occupational safety. General requirements";
- is obliged to conduct or organize training in training rooms
fire-technical minimums with persons (technicians, workers, employees),
the performance of duties associated with increased fire danger
or those responsible for fire safety in departments of the enterprise;
- participates in the investigation, draws up and maintains records of cases
fires, ignitions, victims and deaths in fires, determines
material damage from a fire at an enterprise;
- develops (participates in the development) instructions,
establishing the main directions for ensuring prevention systems
fire and fire protection at the enterprise in accordance with
requirements of GOST 12.1.004, procedure for ensuring the safety of people
and safety of material assets, as well as creating conditions for
successful fire extinguishing;
- bears responsibility for violations of fire safety rules.
2.2. The engineer must:
- prepare orders on the procedure for providing fire protection
security on the territory, in buildings, structures and premises
enterprises, on the appointment of persons responsible for fire safety in
divisions of the enterprise; on the entry into force of instructions, regulations and
recommendations regarding the organization of fire protection of the territory,
buildings, structures, premises and explosive and fire hazardous production facilities
areas of the enterprise;
- develop and implement measures to ensure fire safety
security;
- monitor the maintenance of systems and facilities in good condition
fire protection, including primary fire extinguishing agents, not
allowing them to be used for purposes other than their intended purpose;
- provide the head of the organization with an annual report on
ongoing measures to ensure fire safety and a plan for such
events for next year;
- conduct fire prevention propaganda;
- train employees in fire safety measures;
- report to the manager about violations of standards by employees and other persons
fire safety;
- assist the fire department in extinguishing fires,
establishing the causes and conditions of their occurrence and development, as well as when
identifying persons guilty of violating fire safety requirements and
occurrence of fires;
- provide upon request of government officials
fire supervision information and documents on the state of fire safety
in the organization, as well as about the fires that occurred on its territory and their
consequences;
- immediately inform the head of the organization and the fire department
protection of fires, malfunctions of existing equipment and systems
fire protection, changes in the condition of roads and passages leading
to the place of fire;
- ensure compliance with the requirements of the state fire marshal
supervision relating to its activities and compliance with applicable regulations
ensuring fire safety.
3. Rights of the Engineer.
3.1. The engineer has the right:
- remove from work persons who have not completed fire safety training,
as well as those who showed unsatisfactory knowledge of the basics of fire
security;
- get acquainted with the draft decisions of the organization’s management,
relating to its activities;
- make proposals for optimization and modernization of systems and facilities
fire protection;
- carry out work to establish the causes and circumstances of fires,
what happened in the organization;
- require management to establish measures of social and
economic incentives for workers to increase the level of fire safety
security; 
- receive information on fire safety issues, including
in accordance with the established procedure from management bodies and security units;
- organize and participate in inspections of structural units
organizations to ensure fire safety measures in them,
condition of fire protection means and systems;
- organize and participate in inspections of the organization’s property for
the subject of ensuring fire safety measures when working with it;
- demand from the heads of structural divisions of the organization
information, documents and information relating to its activities;
- demand assistance from the head of the organization and its employees
in performing the functional duties of an engineer and exercising his rights.
4. Responsibility of the Engineer.
4.1. The engineer bears disciplinary liability in accordance with
Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- for improper performance or failure to fulfill their duties;
- for improper condition of fire protection means and systems
In the organisation;
- for causing material damage by one’s actions or inaction
damage in the manner and within the limits established by Art. 238, 239, 241, 243 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- for offenses committed in the course of exercising their
activities in the manner and within the limits established by the current
legislation of the Russian Federation;
- for the reliability of information provided to the management of the organization
and state fire supervision;
- for refusal to carry out the orders and instructions of the manager
organizations;
- for failure to comply with internal regulations;
- for failure to comply with labor safety instructions, official
instructions, safety and fire safety instructions.
5. Working conditions.
The engineer’s work schedule is determined in accordance with the Rules
internal regulations established in the organization.
____________________________________ ____________ _______________________
(position of the head of the organization) (signature) (full name)
I have read the instructions _________________________________ _______________________
(signature) (full name)
<____>____________ 200_ g.
]]> http://www.aup.ru/docs/di/1218.htm ]]>
]]> http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BD%D0%B0%... ]]>
Paper and Internet media Magazine "Human Resources and Personnel Management of the Enterprise", 2011,
Fire safety requirements: what a personnel officer should remember
One of the main responsibilities of the employer is to ensure the safety and working conditions of employees that comply with state regulatory labor protection requirements.
Publication
Personnel officers sometimes forget that this responsibility is to comply not only with labor protection requirements, but also with fire safety rules. Fire safety in Russian legislation is understood as the state of protection of individuals, property, society and the state from fires. Not only the success of passing an inspection by state fire inspection authorities, but also the health, life of workers and the safety of the employer’s property depend on correct compliance with fire safety rules. Let's consider the basic fire safety requirements and determine what a personnel officer should know and remember.
First of all, the personnel service needs to study the legal framework in the field of fire safety, which consists of a number of voluminous documents:
Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 69-FZ “On Fire Safety” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 69-FZ);
Federal Law No. 123-FZ of July 22, 2008 “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 123-FZ);
Fire Safety Rules in the Russian Federation (PPB 01-03), introduced by Order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia dated June 18, 2003 No. 313 (hereinafter referred to as PPB);
Order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated June 20, 2003 No. 323 “On approval of fire safety standards “Design of fire warning systems for people in buildings and structures” (NPB 104-03)” (hereinafter referred to as NPB 104-03);
Order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated June 18, 2003 No. 315 “On approval of fire safety standards “List of buildings, structures, premises and equipment subject to protection by automatic fire extinguishing installations and automatic fire alarms” (NPB 110-03)” (hereinafter referred to as NPB-110-03 );
Order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated December 12, 2007 No. 645 “On approval of fire safety standards “Training in fire safety measures for employees of organizations” (hereinafter referred to as NPB Training);
- “SP 3.13130.2009. Set of rules. Fire protection systems. Warning and management system for evacuation of people in case of fire. Fire safety requirements”, approved by order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2009 No. 173 (hereinafter referred to as SP 3.13130.2009);
- “SP 5.13130.2009. Set of rules. Fire protection systems. Fire alarm and fire extinguishing installations are automatic. Design standards and rules”, approved by order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2009 No. 175 (hereinafter referred to as SP 5.13130.2009);
- “SP 9.13130.2009. Set of rules. Fire equipment. Fire extinguishers. Requirements for operation”, approved by order of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2009 No. 179 (hereinafter referred to as SP 9.13130.2009).
The head of the company also needs to familiarize himself with the above acts, since he directly manages the fire safety system and is personally responsible for compliance with its requirements.
Rights and obligations of the employer and employees in the field of fire safety
The rights and obligations of the employer and employees are defined in the basic document - Law No. 69-FZ.
Heads of the employing organization, including individual entrepreneurs who have entered into employment contracts with employees, in accordance with Art. 37 of Law No. 69-FZ are required to:
Comply with fire safety requirements, as well as comply with orders, regulations and other legal requirements of fire officials;
Develop and implement measures to ensure fire safety;
Conduct fire prevention propaganda, as well as train their employees in fire safety measures;
Include fire safety issues in the collective agreement;
Provide assistance to the fire department in extinguishing fires, establishing the causes and conditions of their occurrence and development, as well as in identifying persons guilty of violating fire safety requirements and causing fires;
Provide, in accordance with the established procedure, the necessary forces and means when extinguishing fires on the territories of enterprises;
Provide access to fire department officials when performing their official duties on the territory, buildings, structures and other facilities of enterprises;
Provide, at the request of officials of the state fire supervision, information and documents about the state of fire safety at enterprises, including the fire hazard of the products they produce, as well as about fires that occurred on their territories and their consequences;
Immediately report to the fire department about fires, malfunctions of existing fire protection systems and means, changes in the condition of roads and passages;
Promote the activities of volunteer firefighters.
Employees in accordance with Art. 34 of Law No. 69-FZ must perform the following duties:
Comply with fire safety requirements;
Have in the premises and buildings in their ownership (use) primary fire extinguishing means and fire-fighting equipment in accordance with fire safety rules and lists approved by the relevant local government bodies;
If fires are detected, immediately notify the fire department;
Before the fire department arrives, take all possible measures to save people, property and extinguish fires;
Assist the fire department in extinguishing fires;
Comply with orders, regulations and other legal requirements of state fire inspection officials;
To provide, in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the opportunity for officials of the state fire supervision to conduct surveys and inspections of production, utility, residential and other premises and buildings belonging to them in order to monitor compliance with fire safety requirements and suppress their violations.
How to organize a fire safety system?
Of the above regulations, the main working document for the employer is the PPB. It is on the basis of this document that a fire safety system should be built in any organization and individual entrepreneur.
In accordance with clause 4 of the PPB, employers at their facilities must have a fire safety system aimed at preventing people from being exposed to dangerous fire factors, including their secondary manifestations. What does this mean?
Order on the procedure for ensuring fire safety
Firstly, the head of the organization or individual entrepreneur must approve the order on the procedure for ensuring fire safety. This order appoints a person responsible for fire safety, approves instructions on fire safety measures, resolves issues of conducting fire safety training, etc. Quite often, farm managers or HR employees are appointed responsible. But no matter who is appointed responsible for fire safety, it is important for the personnel officer to remember that both the head of the organization (individual entrepreneur) and the person responsible for fire safety must undergo fire safety training and receive a certificate of knowledge testing. For each representative office, branch, division or facility of the employer, a person in charge must be appointed who works directly at this facility. A sample order is presented below.
If an employer rents premises, it is important to remember that tenants of premises, in accordance with clause 38 of the PPB, must also comply with fire safety requirements. Therefore, the lease agreement must resolve the issue of the scope of responsibilities in the field of ensuring fire safety rules.
Arbitrage practice
An inspection of compliance with fire safety standards and regulations was carried out in relation to MSE EXPOKHLEB LLC, as a result of which a number of violations of fire safety requirements were identified. The company was brought to administrative liability under Part 1 of Art. 20.4 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The company appealed the decision to the Moscow Arbitration Court on the grounds “that it, as a tenant, was not obliged to ensure compliance with fire safety requirements in the premises it rented.” However, the court considered “that the administrative body has proven that the Company committed an imputed administrative offense, since clause 5.1.1 of the lease agreement... stipulates that MSE EXPOKHLEB LLC is responsible for compliance with fire safety requirements in the premises it occupies.”
The Ninth Arbitration Court of Appeal (resolution No. 09AP-11476/2011-AK dated May 31, 2011 in case No. A40-22404/11-119-165) confirmed the legality of the decision of the Moscow Arbitration Court. The resolution states: “LLC MSE “EXPOKHLEB”, listing in appeal the violations charged against him, indicating the norms of the Rules, did not provide justification that he had complied with the specified fire safety requirements or that the obligation to comply with them did not apply to the Company.
The Company’s reference to the fact that it leases premises for an office, and not warehouse premises, to which the administrative body referred in procedural documents as premises in which the identified violations were committed, is not accepted by the court of appeal, since from clause 1.1 of the lease agreement. .. it follows that LLC MSE "EXPOKHLEB" has also been provided with ancillary premises for rent.
Paragraph 2 of PPB 01-03 provides that organizations, their officials and citizens who violate fire safety requirements are liable in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Part 1 of Article 20.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes that violation of fire safety requirements entails administrative liability.
Taking into account the above, the appellate court considers it proven that the Company committed the administrative offense imputed to it.”
Instructions on fire safety measures
The second important element of the fire safety system is instructions on fire safety measures. According to clause 6 of the PPB, at each facility such instructions must be developed for each explosion-hazardous and fire-hazardous area. In addition, clause 14 of the PPB contains reference to general facility instructions. Therefore, the employer should develop and approve general instructions for each facility, and if such a facility has an explosive or fire-hazardous area, create separate instructions for these areas. Instructions on fire safety measures are local normative act, with which it is necessary to familiarize all employees with a personal signature, and newly hired employees must be familiarized with this act with a personal signature even before concluding an employment contract.
The instructions on fire safety measures must reflect the following information (Appendix 1 to PPB 01-03):
1) the procedure for maintaining the territory, buildings and premises, including evacuation routes;
2) measures to ensure fire safety during technological processes, equipment operation, and fire hazardous work;
3) the procedure and standards for storage and transportation of explosive substances and fire hazardous substances and materials;
4) places of smoking, use of open fire and hot work;
5) the procedure for collecting, storing and removing flammable substances and materials, maintaining and storing protective clothing;
6) limit readings of control and measuring instruments (pressure gauges, thermometers, etc.), deviations from which may cause a fire or explosion;
7) duties and actions of workers in case of fire:
Rules for calling the fire department;
Procedure for emergency shutdown of process equipment;
The procedure for turning off ventilation and electrical equipment;
Rules for the use of fire extinguishing means and fire automatic installations;
Procedure for evacuation of flammable substances and material assets;
The procedure for inspecting and bringing all premises of the enterprise (division) into a fire and explosion-proof condition.
When developing instructions, it is also necessary to pay attention to clause 15 of the PPB, which contains a list of issues that should be reflected in the employer’s administrative document, in particular:
Determining the location and permissible quantity of raw materials, semi-finished products and finished products located in the premises at one time;
Determining the procedure for de-energizing electrical equipment at the end of the working day;
Regulation of the procedure for inspection and closure of premises after completion of work;
Determining the procedure and timing of fire safety training and fire safety training, as well as appointing those responsible for their implementation.
Since clause 15 of the PPB does not specify the type of document, some of the issues can be stated not in the instructions, but in the order on the procedure for ensuring fire safety.
In addition, when drawing up instructions, you need to pay attention to clause 110 of the Fire Safety Regulations, which describes specific actions that the head of the organization (individual entrepreneur) or the person responsible for fire safety should take upon arrival at the scene of the fire. Such actions include reporting the occurrence of a fire to the fire department, organizing the rescue of people in the event of a threat to their lives, checking whether the fire warning system, fire extinguishing, smoke protection is activated, turning off power if necessary, stopping the operation of transporting devices, units, apparatus, stopping all work in the building, removal of workers from the danger zone, organization of evacuation and protection of material assets, etc. It is advisable to specify the above actions more fully and specifically in the instructions developed by the employer.
The HR department needs to remember that job descriptions persons responsible for fire safety must contain appropriate responsibilities. If the responsibilities for ensuring fire safety are assigned to an employee in order to combine positions, then the order for such combination must list the employee’s responsibilities and the amount of additional payment for the combination.
Other PPB requirements
As the third element of the employer’s fire safety system, we list a number of fire safety requirements. Thus, clause 13 of the Rules requires that in all premises there should be posted signs indicating the fire department telephone number.
According to paragraph 16 of the PPB in buildings and structures where more than 10 people are on the floor at a time, they must be developed and posted in prominent places plans (schemes) for evacuation of people in case of fire, and also provides fire warning system (installation). The fire warning system (installation) must comply with NPB 104-03 and SP 3.13130.2009. Section 5 of NPB 104-3 will help an individual entrepreneur determine the type of warning system and control of evacuation of people in case of fire. In buildings where technical means of notifying people about a fire are not required, an individual entrepreneur must determine the procedure for notifying people about a fire and appoint persons responsible for this (clause 103 of the PPB).
If 50 people or more are simultaneously staying at the site of an individual entrepreneur, then in addition to the schematic plan for evacuation of people in case of fire, a instructions defining the actions of personnel for safe and quick evacuation, which should be carried out at least once every six months practical evacuation training all employees.
At the same time, the PPB in paragraph 52 requires that doors on evacuation routes open freely and in the direction of exit from the building.
Employers should also remember to ensure timely maintenance and inspection fire protection systems and installations. In accordance with clause 34 of the PPB, they must be kept in working order at all times. The list of premises and equipment that must be equipped with automatic fire extinguishing installations (AUP) and fire alarm systems (AUPS) is given in NPB 110-03.
According to clause 23 of the PPB, roads, driveways and entrances to buildings, structures, open warehouses, external fire escapes and water sources used for fire extinguishing, must always be free to travel fire equipment , maintained in good condition, and in winter cleared of snow and ice. Standard safety signs must be posted near equipment that has an increased fire hazard (clause 33 of the PPB).
Clause 40 of the Rules contains a number of prohibitions on the storage of flammable and combustible liquids, explosives and so on. in basements and ground floors, placement of storage rooms, kiosks and stalls in elevator halls, etc. prohibitions. A number of restrictions have also been established when operating evacuation routes and exits: do not block the paths, do not block the doors, do not install dryers and clothes hangers in the vestibules of the doors, do not install thresholds, revolving doors and turnstiles, etc. (clause 53 of the PPB). PPB also impose requirements for the maintenance of external fire escapes and fences on the roofs of buildings and structures. They must be kept in good condition and subjected to operational tests at least once every five years (clause 41 of the PPB). The doors of attics, as well as technical floors and basements where permanent presence of people is not required, must be locked. On the doors of these premises there should be information about where the keys are stored. Windows in attics, technical floors and basements must be glazed and permanently closed (clause 44 of the PPB).
In accordance with clause 108 of the PPB, premises, buildings and structures must be provided primary fire extinguishing agents (fire extinguishers and etc.). The procedure for determining the required quantity, types and types of such funds are established in Appendix No. 3 to the PPB.
Failure to comply with the above and other requirements of the PPB may result in administrative liability.
Example
In the summer of 2008, LLC A, which rented premises in a business center in Moscow, held scheduled inspection compliance with fire safety requirements. During the inspection, a number of violations of fire safety requirements were identified, namely:
In all administrative, warehouse and auxiliary premises, signs indicating the fire department telephone number were not posted in visible places (clause 13 of the PPB);
Access to the interior cabinet was difficult fire-fighting water supply(clause 40 of the PPB);
It was allowed to obstruct evacuation routes (staircase) with furniture (clause 53 of the PPB);
Some premises were not equipped with fire protection systems (automatic fire extinguishing and alarm systems) (clause 6 of NPB 110-03).
The state fire inspector drew up a protocol on administrative violation. The company was issued an order to eliminate violations of fire safety requirements, which specified the following measures to eliminate violations:
In all administrative, warehouse and auxiliary premises, place signs in visible places indicating the fire department telephone number;
Provide unobstructed access to the internal fire water supply cabinet;
Clear escape routes (stairwell) from furniture;
All premises to be protected should be equipped with fire protection systems (automatic fire alarms, fire sprinklers).
An unscheduled inspection was carried out to monitor compliance with the order. In addition, the company was subjected to administrative punishment in the form of a fine in the amount of 20,000 rubles. (Please note that since June 17, 2011, the amount of fines has increased significantly.)
Fire safety training
Law No. 69-FZ establishes the obligation of the employer’s administration to train its employees in fire safety measures. The head of the organization, individual entrepreneur responsible for fire safety are responsible for the organization and timeliness of training in the field of fire safety and testing the knowledge of fire safety rules for employees (clause 2. NPB Training). Employees are also responsible for the timeliness of training and do not have the right to avoid completing such training. Fire safety training is informing society and citizens about fire safety requirements, including measures to prevent fires, organizing fire extinguishing, as well as actions to save lives and property in the event of fires 1 .
In practice, as a rule, fire safety training only refers to fire safety instruction. However, the personnel officer must remember that such an interpretation is not entirely correct. According to clause 4 of the NPB Training, the main types of training for employees of organizations in fire safety measures are fire safety briefing and the study of the minimum fire-technical knowledge (hereinafter referred to as the fire-technical minimum, PTM).
The head of the organization (individual entrepreneur), its specialists and employees responsible for fire safety must be trained fire technical minimum. Such training is carried out within one month after hiring and then at least once every three years, and in fire and explosion hazardous industries - at least once a year. The responsibility for organizing minimum fire safety training rests with the employer. The head of the organization, his main specialists and employees responsible for fire safety must undergo PTM training outside of work on the basis of concluded agreements with specialized institutions (for example, training centers of the Federal Fire Service of the Ministry of Emergency Situations) according to fire-technical minimum programs. In this regard, the personnel service must:
Compile lists of persons to be trained in PTM;
Organize a search educational institution and concluding training agreements with him (after checking that they have the necessary documents);
Prepare documents for sending employees to off-the-job training.
In accordance with clause 7 of the PPB, all employees must be allowed to work only after passing fire safety training. The procedure is regulated by the NPB Training. The purpose of fire safety briefing is to inform workers of the basic fire safety requirements, study the fire hazard of technological processes of production and equipment, fire protection equipment, as well as their actions in the event of a fire.
Fire safety training is carried out with all employees according to approved programs and in the manner determined in the local act of the employer. The procedure for conducting fire safety training may be established by a separate act or Instruction on fire safety measures, and the employer must approve the programs by order, for example, an order on the procedure for ensuring fire safety.
During the briefing process, taking into account the specifics of the company’s activities, employees must be familiarized with:
With rules for maintaining the territory, buildings and premises, including evacuation routes, external and internal water supply systems, fire warning systems and management of the evacuation process;
Fire safety requirements;
Measures to ensure fire safety during the operation of buildings, equipment, and the performance of fire hazardous work;
Rules for the use of open fire and hot work;
Responsibilities and actions of workers in case of fire, rules for calling the fire department, as well as the use of fire extinguishing equipment and fire automatic installations.
In accordance with the NPB Training, there are 5 types of fire safety briefings: introductory, primary at the workplace, repeated, unscheduled and targeted. They all differ in nature and timing. In accordance with clause 10 of the NPB, the employer must conduct training log of fire safety briefings, the form of which is approved by Appendix No. 1 to the NPB Training. This journal contains entries about the conduct of introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled, targeted fire safety briefings with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing.
Introductory fire safety briefing, according to clause 11 of the NPB Training is carried out:
With all employees of the organization who are newly hired, regardless of their education and length of service in the profession (position);
With seasonal workers;
With employees seconded to the organization;
With students arriving for on-the-job training or internship;
Introductory briefing is carried out directly by the head of the organization or the person responsible for fire safety in a specially equipped room using visual aids and educational materials. The introductory fire safety briefing program should be developed taking into account the approximate list of questions approved by Appendix No. 2 of the NPB Training. Such instruction ends with practical training of actions in the event of a fire and testing of knowledge of fire extinguishing equipment and fire protection systems.
Conducted directly at the workplace primary fire safety briefing with all newly hired employees, with employees transferred from one division to another; with employees performing work that is new to them; with employees seconded to the organization; with seasonal travelers; with on-the-job trainees or trainees, etc. (clause 16 of the NPB Training). The NPB Training states that such instruction is carried out by the person responsible for fire safety in each structural unit, but if the organization has a small staff and does not have departments, then the manager himself or the person entrusted with the responsibilities of the person responsible for fire safety can instruct. Initial training is carried out personally with each employee. At the same time, the employee is explained, demonstrated visually and practiced with him the ability to use primary fire extinguishing means (usually fire extinguishers), actions in the event of a fire, evacuation rules, and assistance to victims. As in the case of introductory briefing, an approximate list of questions approved by Appendix No. 2 of the NPB Training will help develop an initial briefing program.
In order to test knowledge of fire safety, the person responsible for fire safety conducts repeated fire safety training at least once a year, and with employees of organizations with fire-hazardous production, at least once every six months in accordance with the training schedule approved by the individual entrepreneur.
In a number of cases listed in paragraph 26 of the NPB, Training must be carried out unscheduled fire safety briefing, For example:
When introducing new or changing previously developed rules, regulations, and instructions on fire safety;
When changing the production process, replacing or upgrading equipment, tools, raw materials, materials;
If employees of the organization violate fire safety requirements, which could or have led to a fire;
When establishing facts of unsatisfactory knowledge by employees of organizations of fire safety requirements, etc.
Unscheduled briefing is carried out by the employee responsible for ensuring fire safety, while the volume and content of the briefing are determined in each specific case, depending on the reasons that necessitated the need for it.
In the case of one-time welding and other hot work, liquidation of the consequences of accidents, preparation of mass events with the number of participants more than 50 people and other cases (clause 28 of the NPB Training) is carried out targeted fire training.
Responsibility for violation of fire safety requirements
For violation of fire safety requirements, an organization and an individual entrepreneur may be brought to administrative and criminal liability.
In accordance with Art. 38 of Law No. 69-FZ, responsibility for violations of fire safety requirements lies with property owners, persons authorized to own, use or dispose of property, including heads of organizations, persons responsible for ensuring fire safety, as well as officials within their competence. Since responsibility for fire safety is often assigned to personnel employees, the provisions of the above article also apply to them, as officials.
Administrative liability for violation of fire safety requirements is established by Art. 20.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which has been in force since June 17, 2011 in a new, more stringent version. In addition, the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation contains sanctions for violation of fire safety rules in forests (Article 8.32) and for violation of fire safety requirements in railway, sea, inland water and air transport (Article 11.16 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). We must not forget about the provisions of Art. 19.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation of liability for failure to comply on time with a legal order (resolution, presentation, decision) of the body (official) exercising state supervision (control).
Criminal liability for violation of fire safety requirements is established by Art. 219 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In conclusion, it is necessary to emphasize once again that compliance with fire safety requirements is important not only as a guarantee against claims from inspection bodies and prosecution, but also as a guarantee of safety and prevention of the threat of destruction and damage to the employer’s property, and, most importantly, a threat to the life and health of its employees .



















